Fig 2.
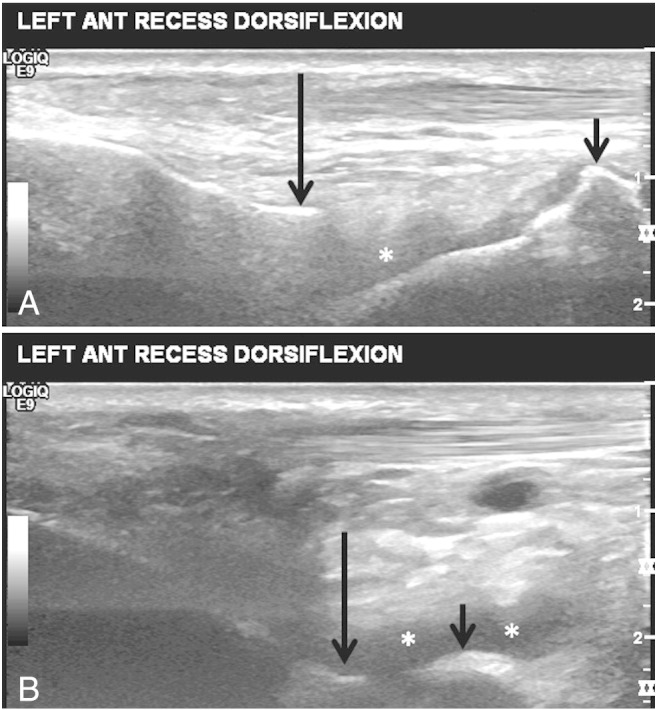
Images taken from a cine of ankle dorsiflexion with the US transducer in long axis to the tibia. Image A is the beginning of dorsiflexion. Note the hyperechoic tibial cortex (long arrow) and hyperechoic degenerative talar ridging (short arrow). A small amount of hypoechoic joint fluid is also seen (asterisk). At end-range dorsiflexion (image B), appreciate the near abutment of the tibia (long arrow) and talar ridges (short arrow). Also, there has been a modest increase in the amount of joint fluid (asterisks). Visualization of abutment of these bony structures correlated with the patient’s symptom of anterior ankle pain, a finding consistent with an impingement syndrome.
