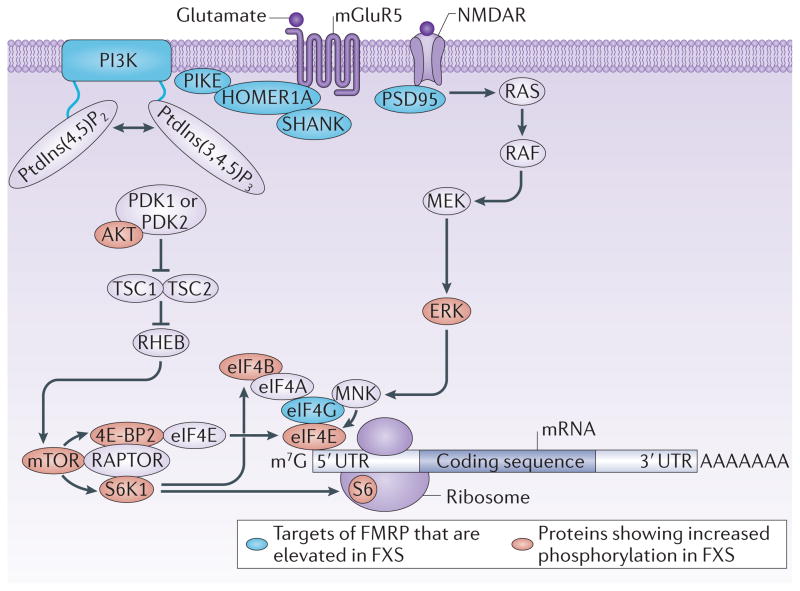
Figure 1. Translational control pathways that are dysregulated in FXS.
Normally, stimulation of cell surface receptors, including NMDA receptors (NMDARs) and group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs; such as mGluR5), results in the activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)23,94, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1; which comprises mTOR bound to regulatory-associated protein of mTOR (RAPTOR))37 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)77 signalling pathways in neurons. mTORC1 phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) binding proteins (4E-BPs), including 4E-BP2, the predominant 4E-BP isoform in the mouse brain, which derepresses eIF4E to promote ‘cap’-dependent translation. mTORC1 also phosphorylates and activates p70 S6 kinase 1 (S6K1), which phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6 and eIF4B. Phosphorylation of eIF4B by S6K1 stimulates the helicase activity of eIF4A to promote cap-dependent translation. mTORC1-dependent translation is triggered upstream by a signalling pathway involving PI3K, 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) and/or PDK2, AKT, tuberous sclerosis 1 (TSC1) and/ or TSC2 and RAS homologue enhanced in brain (RHEB). ERK phosphorylates and activates MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinases (MNKs), which phosphorylate eIF4E to promote translation. This ERK-dependent translation is triggered upstream by a pathway involving RAS, RAF and MAPK/ERK kinase 1 (MEK1). mGluR5 signals to the PI3K–AKT–mTORC1 pathway via HOMER1A, SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains (SHANK) proteins and PI3K enhancer (PIKE), and NMDARs signal to ERK via postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD95). The protein levels of several targets of the RNA-binding protein fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP)67,68 are increased in fragile X syndrome (FXS). The increased expression of these proteins results in basally elevated PI3K, mTORC1 and ERK signalling and thus increased translation. m7G, 7-methyl-guanosine; PtdIns(4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate; PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate; UTR, untranslated region. Adapted from REF. 5, Nature Publishing Group.