Fig. 2.
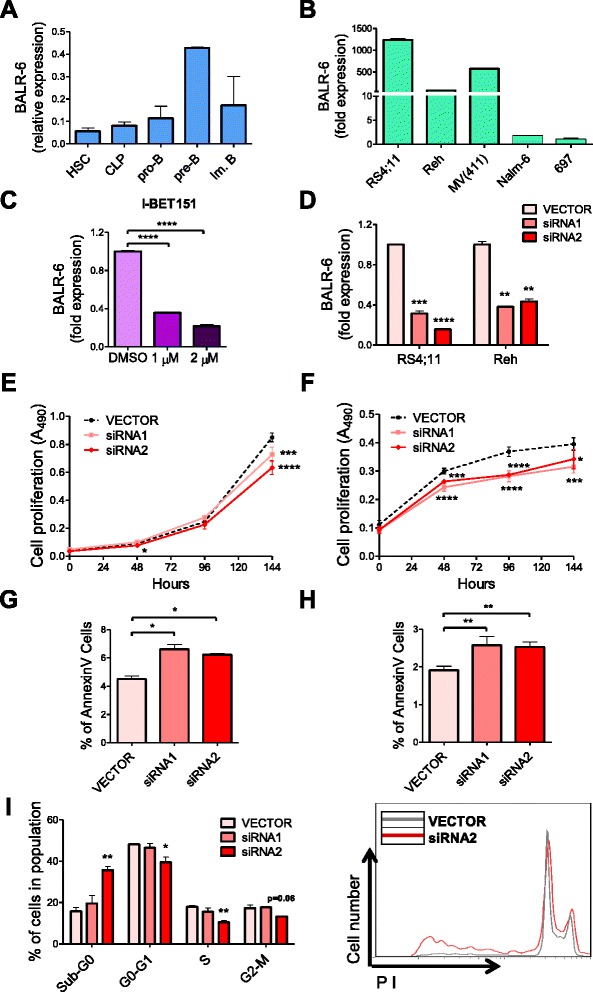
BALR-6 knockdown reduces cell proliferation and increases apoptosis in human B-ALL cells. a BALR-6 expression in human bone marrow B-cell subsets by qRT-PCR. Normalized to ACTIN. b Quantitation of BALR-6 expression in human B-ALL cell lines by qRT-PCR confirming elevated levels in MLL translocated cell lines RS4;11, and MV(411). Normalized to ACTIN. c RS4;11 cell lines treated with 1 μM, and 2 μM of I-BET151 inhibitor for 36 h, presented a decrease in BALR-6 expression levels. Normalized to ACTIN. d qRT-PCR quantification of BALR-6 in RS4;11 and Reh cell lines transduced with vector control, siRNA1 or siRNA2. Normalized to ACTIN. e, f Decreased cell proliferation, upon siRNA mediated knockdown of BALR-6 in RS4;11 cells e, and Reh cells f as measured by MTS. g, h AnnexinV staining showed that siRNA mediated knockdown of BALR-6 in RS4;11 cells g, and Reh cells h resulted in an increase of apoptosis. i Propidium iodide staining of RS4;11 knockdown cell lines showed an increase in Sub-G0 and a decrease in G0-G1, S and G2-M cells. Representative histogram of (i) confirms cell cycle changes by siRNA2, shown to the right. HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; CLP, common lymphoid progenitor; pro-B, progenitor B; pre-B, precursor B; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. Evaluations were made using a two-tailed T-test, p < 0.05 (*); p < 0.005 (**); p < 0.0005 (***); p < 0.0001 (****)
