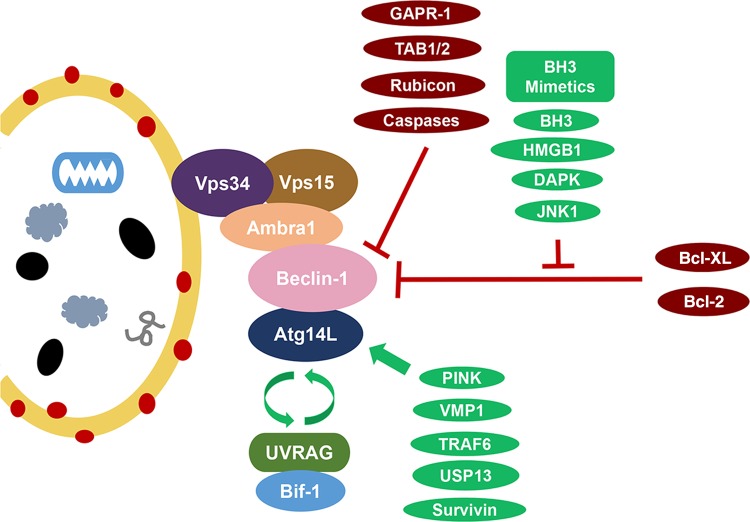
Figure 1.
Beclin-1 interaction complexes Atg14L and UVRAG/Bif-1 activate the Beclin-1 complexes and induce the formation of autophagosomes in a mutually exclusive manner. UVRAG also potentially functions to promote autophagosome maturation and endocytic trafficking through pathways independent of its interaction with Beclin-1. VMP-1 and PINK1 are two other interacting partners and inducers of autophagy. NIF-1 is a component of the PI3K complex contributing to the interaction of Beclin-1 and Bcl-2 at the ER surface. Bcl-2/Bcl-XL has similar function in Beclin-1 binding and autophagy inhibition. JNK1 and DAPK are autophagy inducers that phosphorylate Bcl-2 and Beclin-1, respectively, to disrupt their interaction with each other. HMGB1 (high-mobility group box 1), a p53 interacting chromatin protein, induces autophagy for cell protection against damage in a similar fashion. TRAF6 and USP13 are reported to play a role in Beclin-1 ubiquitination. Survivin is a Beclin-1-binding anti-apoptotic protein to regulate TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Rubicon binds Beclin-1 to inhibit autophagosome formation and maturation. Dissociation of upstream activators TAB1/2 in TAK1-IKK pathway is thought to be necessary for autophagy induction. GAPR-1 binds Beclin-1 to inhibit autophagy; however, the mechanism is not entirely clear.