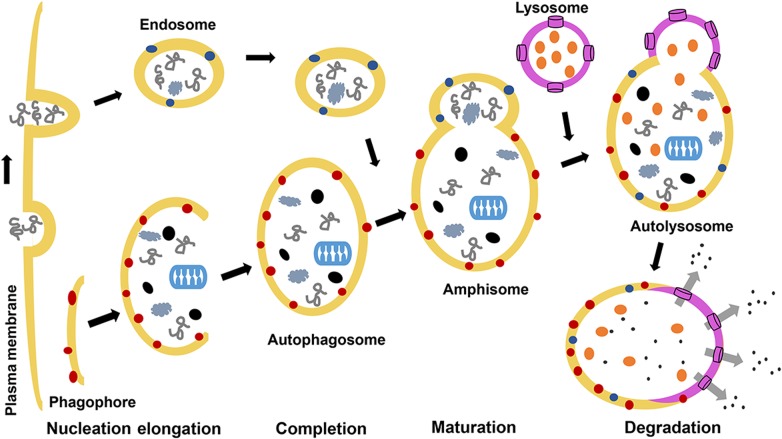
Figure 2.
General stages of autophagy Autophagy is characterized by the induction of phagophore by the ULK complex, which is activated by being liberated from the mTORC1 complex due to its inactivity. This dissociation event results in the dephosphorylation of inhibitory sites of Ulk1/2 and autophosphorylation of its activating sites, which leads to concomitant activation of its interacting partners mAtg13 and FIP200 and localization of the ULK complex from the cytosol to the ER. Activation of the ULK complex also mediates the activation and ER assembly of class III PI3K complex that consists of Beclin-1, Vps34, and p150 during the nucleation phase [16]. Complete elongation of the phagophore generates a structure called ‘autophagosome’, and this process involves two ubiquitin-like conjugation pathways. The autophagosome sequesters its cargo and fuses with the lysosome on a Beclin-1-dependent manner to form the lysoautophagosome and where the contents are digested by lysosomal enzymes for degradation or recycle. Details are provided in the text.