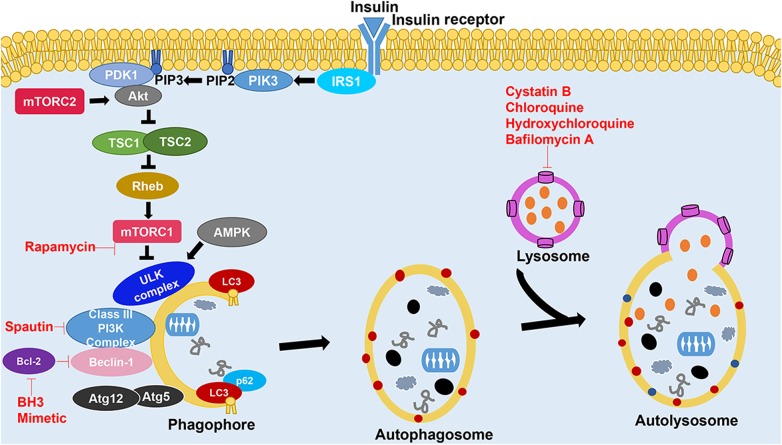
Figure 3.
Autophagy and some of its regulatory pathways Binding of insulin or growth factors to the insulin receptor triggers the PI3K pathway, converting PIP2 into PIP3 that recruits PDK1 and Akt to the plasma membrane. Activation of Akt by insulin binding or direct mTORC2 stimulation inactivates TSC1/2 (tuberous sclerosis 1/2) [25], resulting in the activation of Rheb and mTORC1. Under starvation or rapamycin application, Ulk1 is phosphorylated by AMP-activated protein kinase and detaches from mTORC1 complex, rendering it inactive and triggers the autophagy pathway. The mTORC1 complex and AMP-activated protein kinase sense the nutrient state of the cell and accordingly maintains homeostasis by controlling levels of amino acids through various pathways, including autophagy. LC3 mediates selective autophagy by recruiting several adapter proteins, including p62, to the autophagosome. The activity of PI3K complex can be manipulated by several pharmacological modulators such as activators like BH3 mimetics and inhibitors such as spautin-1. Other modulators of autophagy are also shown in the figure.