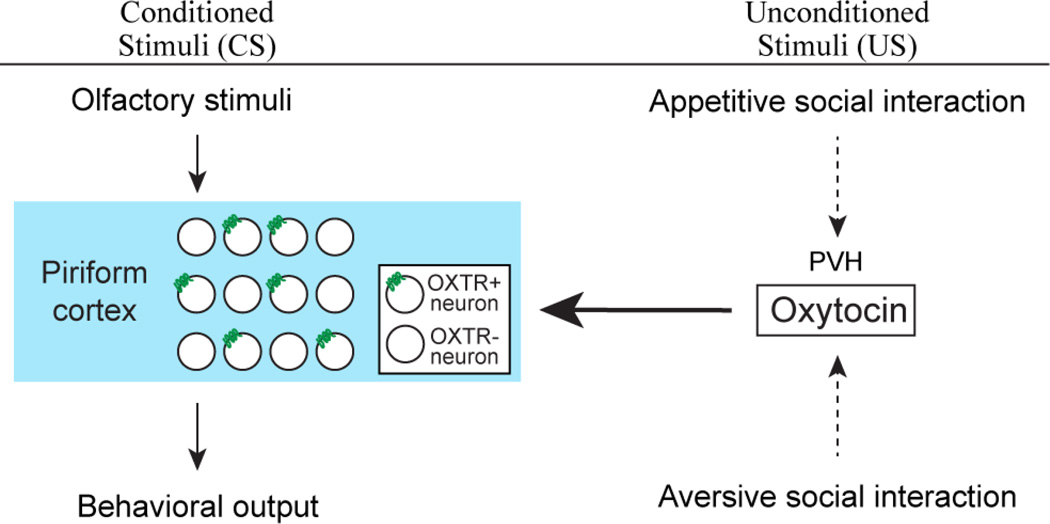
Figure 7.
Model for entrainment of odor to social cues of opposing valence. Associative learning transforms initially neutral olfactory representations (CS) in the piriform cortex to produce learned behavioral responses. Oxytocin, representing saliency of social cues of both appetitive and aversive nature (US), modulates this process by directly impacting the piriform cortex.