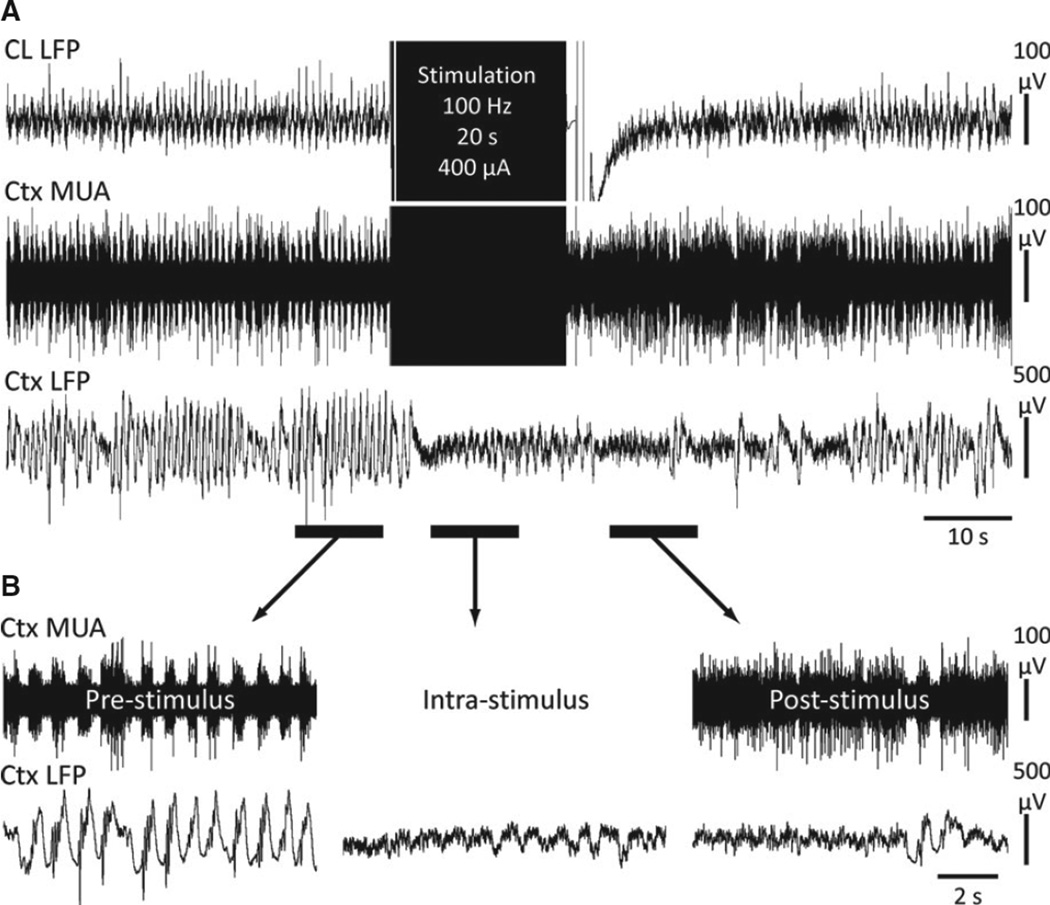
Figure 1.
Central lateral thalamic stimulation during deep anesthesia decreases cortical slowing and increases cortical neuronal firing. (A) Example stimulation of CL under deep ketamine/xylazine anesthesia. (B) Magnified insets of the marked pre-, intra-, and poststimulus epochs exemplify desynchronized cortical LFP intrastimulus which is persistent post-stimulation and is then associated with sustained tonic cortical MUA. Ctx, frontal cortex; CL, central lateral thalamus; MUA, multiunit activity; LFP, local field potential.
Epilepsia © ILAE