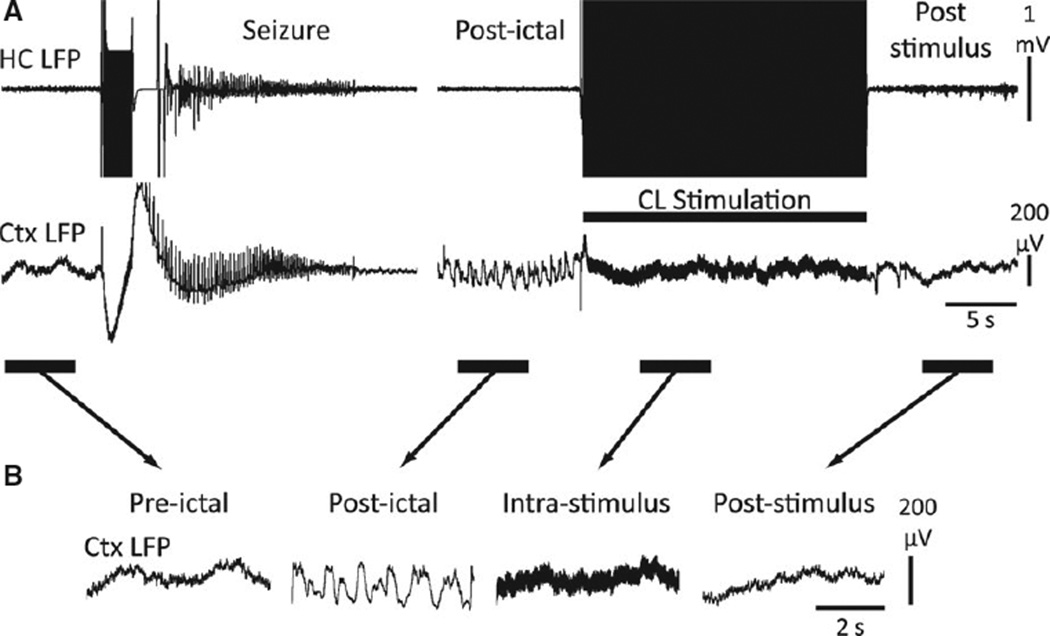
Figure 5.
Thalamic CL stimulation in the postictal period abolishes cortical slow-wave activity. (A) Example of central lateral thalamic stimulation in the postictal period after a secondarily generalized seizure in an awake-behaving animal. Break in recording display is 255 s to show postictal slow-wave activity just prior to CL stimulation. (B) Magnified insets of the indicated preictal, postictal, intrastimulus, and poststimulus epochs. Cortical slow waves are seen in the “postictal” epoch, which is dramatically reduced during “intrastimulus” and “poststimulus” epochs. The poststimulus epoch resembles the baseline preictal epoch. HC, hippocampus; CL, central lateral thalamus; Ctx, frontal cortex; LFP, local field potential.
Epilepsia © ILAE