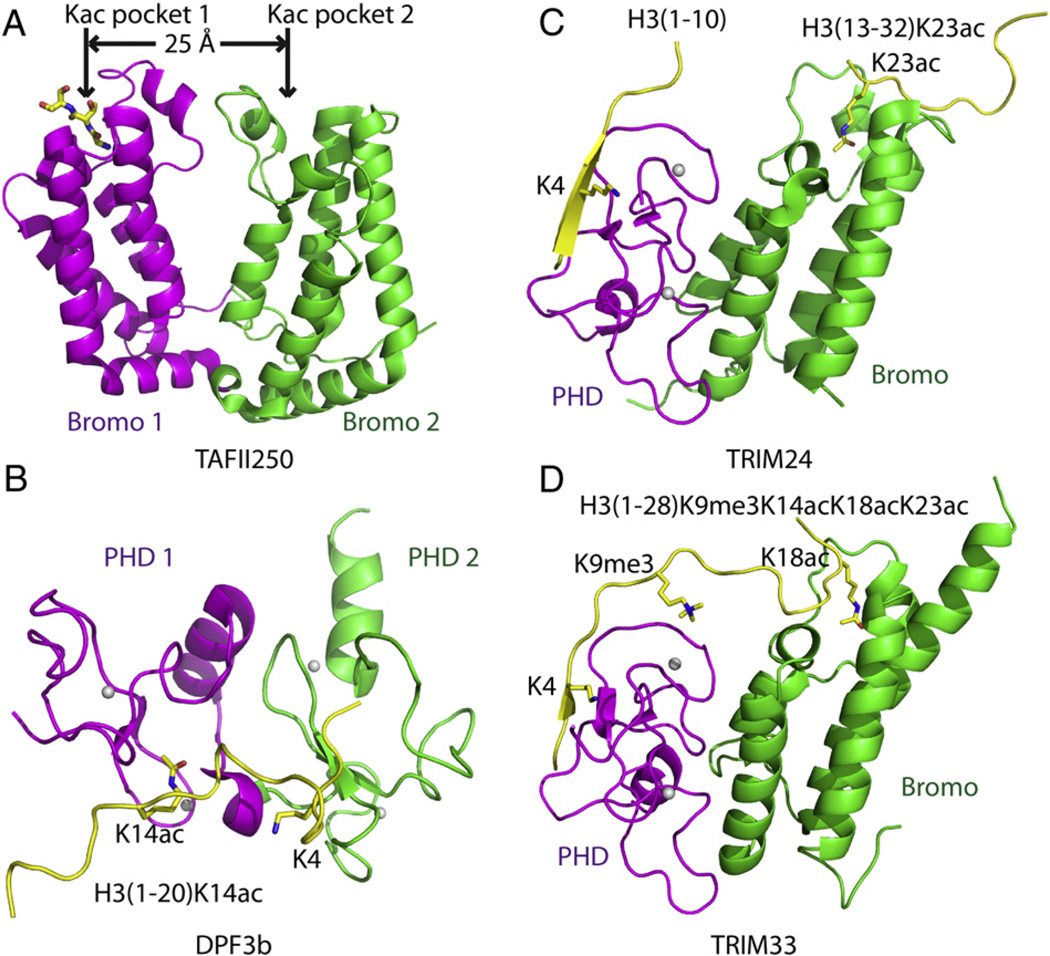
Fig. 1.
Structural basis for multivalent readout of histone marks from a single histone tail. (A) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of TAFII250 double bromodomain (PDB code: 1EQF) with bromodomain 1 colored in magenta and bromodomain 2 in green. The N-terminus of a symmetry related protein inserts into the acetyllysine (Kac) binding pocket of bromodomain 1. The distance between two Kac binding pockets of the two bromodomains is 25 Å. (B) Ribbon representation of the solution NMR structure of DPF3b double PHD fingers in complex with H3(1–20)K14ac peptide (PDB code: 2KWJ)with PHD1 finger colored in magenta, the PHD2 finger in green, and the bound peptide in yellow. The zinc ions are shown as silver balls. The specific residues recognized on the H3 peptide, including K4 and K14ac, are highlighted in stick representations. (C) Ribbon-representation model of TRIM24 PHD-Bromo cassette simultaneously recognizing unmodified H3K4 and H3K23ac following superposition of the crystal structures of TRIM24 PHD-Bromo-H3(1–10) complex (PDB code: 3O37) and TRIM24 PHD-Bromo-H3(13–32)K23ac complex (PDB code: 3O34). The PHD finger, bromodomain and bound peptides are colored in magenta, green and yellow, respectively. The unmodified H3K4 and H3K23ac are highlighted in stick representations. (D) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of TRIM33 PHD-Bromo cassette in complex with H3(1–28)K9me3/K14ac/K18ac/K23ac peptide (PDB code: 3U5O and 3U5P) with the PHD finger, bromodomain, and bound peptide colored in magenta, green and yellow, respectively. The unmodified H3K4, H3K9me3 and H3K18ac, which are specifically recognized, are highlighted in stick representations.