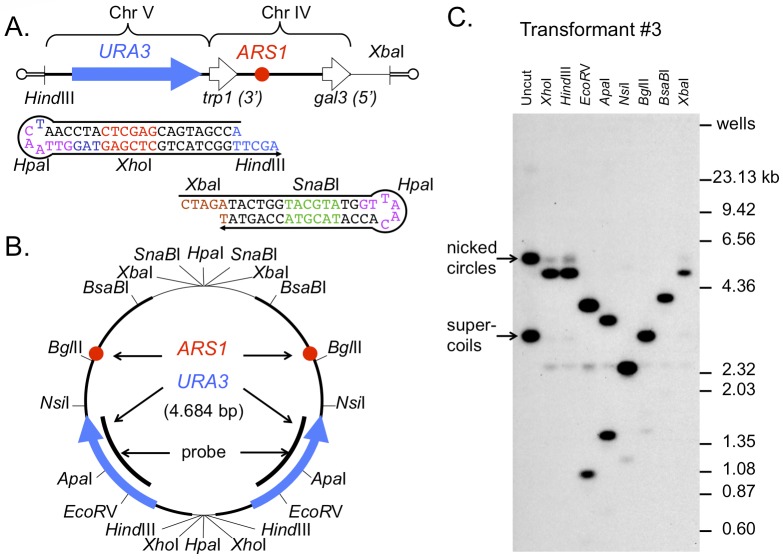
Fig 4. Transformation of yeast with an artificial dog bone results in inverted dimeric plasmids.
(A) A HindIII-XbaI restriction fragment from plasmid pUA-DirB contains the URA3 gene from chromosome V (blue arrow) and the origin ARS1 from chromosome IV (red circle). Oligonucleotide hairpins were designed with HindIII (blue) and XbaI (brown) overhangs, 5’-phosphates to ensure their ligation to the ends of the URA3-ARS1 fragment, and additional restriction sites in the duplex and loop portions to facilitate analysis of the DNA after transformation. (B) Map of the anticipated inverted dimeric plasmid after transformation and replication in yeast. Cleavage sites are indicated in bp. (C) Eight transformants were chosen at random; all eight had plasmids and five (transformants 1, 3, 5, 7, and 8) had restriction maps that were consistent with the map expected for a circular inverted dimer. The Southern blot using a URA3 probe for transformant #3 is shown.