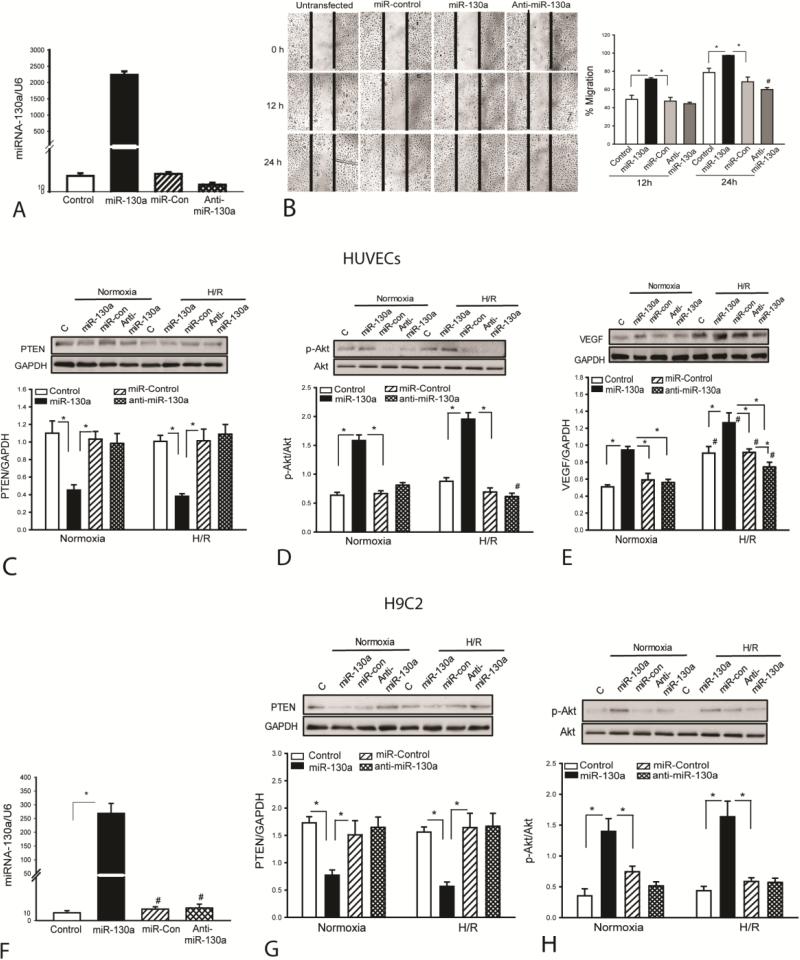
Figure 5.
MiR-130a promotes endothelial cell migration, suppresses PTEN expression and increases Akt phosphorylation. HUVECs and H9C2 cardiomyoblasts were transfected with miR-130a mimics, scrambled miR-control mimics, or anti-miR-130a mimics, respectively. Twenty four hours after transfection, cells were subjected to hypoxia (4 h) followed by reoxygenation (24 h). The cells that were cultured at normal condition served as control (normoxia). (A) Increased miR-130a levels in HUVECs 48 h after transfection of miR-130a mimics. (B) Transfection of miR-130a mimics promotes HUVEC migration into the wound area. Representative images were taken before, 12 and 24 hours after injury (×4 magnification). Dashed line indicates the width of gap. N=3/group. #p<0.05 compared to all other groups. Transfection of miR-130a mimics suppresses PTEN expression (C), increases Akt phosphorylation (D) and VEGF expression (E) in HUVECs. Transfection of miR-130a mimics increases the levels of miR-130a (F), suppresses PTEN expression (G) and increases Akt phosphorylation (H) in H9C2 cardiomyoblasts . N=3-4 in each group. *p<0.05 compared with indicated group. #p<0.05 compared with other groups.