Figure 1.
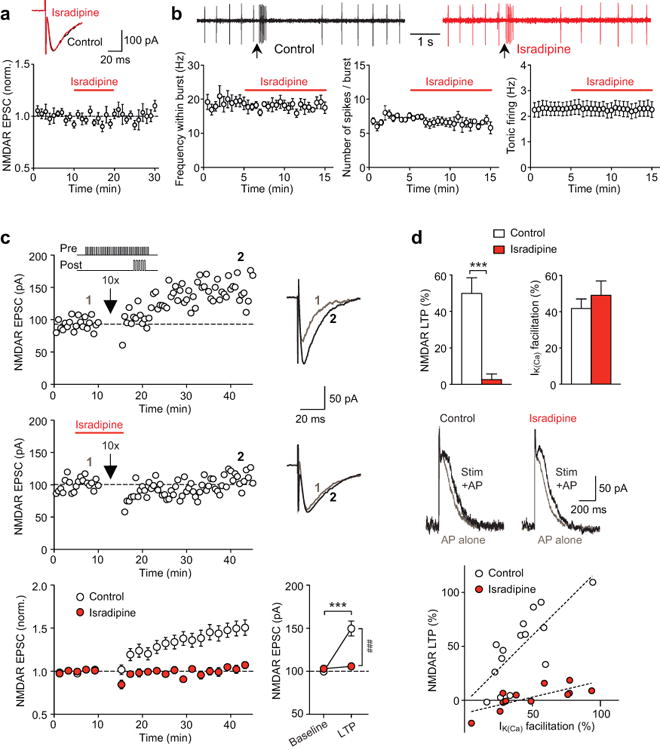
Isradipine blocks NMDAR LTP induction in the VTA. (a) Isradipine (2 μM) had no effect on NMDAR EPSCs (n = 6 cells; example EPSC traces before and after isradipine application). (b) Example traces (top; aspartate iontophoresis at arrows) and summary time graphs (bottom) illustrating that isradipine had no effect on the frequency/number of spikes within the burst (n = 5 cells) or tonic firing (n = 8 cells). (c) Example experiments (EPSC traces at the times indicated) and summary time graph showing that isradipine blocked the induction of NMDAR LTP. Graph at the bottom right depicts average EPSC amplitude during baseline and after LTP (F1,25 = 21.89, p < 0.001, n = 12–15 cells/group; mixed two-way ANOVA). ***p < 0.001 vs. baseline; ###p < 0.001 between groups (Bonferroni post hoc test). (d) Isradipine blocked LTP induction without affecting synaptic facilitation of IK(Ca). Data are from the same cells shown in (c) (LTP: t25 = 4.71, p < 0.001; IK(Ca) facilitation: t25 = 0.79, p = 0.43; unpaired t test). Example traces depict IK(Ca) evoked by a single AP alone and with preceding synaptic stimulation. Bottom graph illustrates the relationship between LTP magnitude and the degree of IK(Ca) facilitation obtained from each cell (dashed lines: linear fit to all data points in each group).
