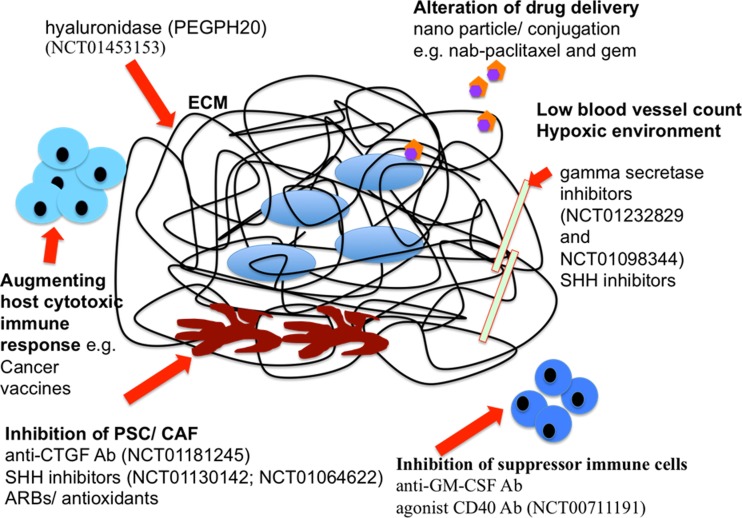
Fig. 2.
Diagrammatic representation of tumor microenvironment in PDA with new therapeutic targets. Ab antibody, CAF cancer-associated fibroblast, CTGF connective tissue growth factor, ECM extracellular matrix, GM-CSF granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, PDA pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, PSC pancreatic stellate cell, SHH sonic hedgehog, nab-paclitaxel albumin-bound paclitaxel, ARB angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker. Red arrows indicate the site of action. 1. PSC and CAF can be targeted by inhibition of SHH, CTGF, and ARBs. 2. ECM components lead to desmoplasia, creating barriers for drug delivery that can be circumvented by drug alteration and conjugation such as nab-paclitaxel and human recombinant PEGylated hyaluronidase (PEGPH20). 3. Tumor vessels are compressed by dense tumor stroma, resulting in a hypoxic environment; tumor vasculature can be targeted by SHH and gamma-secretase inhibitors. 4. Suppressor immune cells can be targeted by agonist CD40 antibodies or anti-GM-CSF antibodies. 5. Host immune response can be strengthened by cancer vaccines such as GVAX pancreas prime and Listeria monocytogenes-expressing mesothelin (CRS-207) boost vaccines [67]. 6. Selected ongoing and recently completed clinical trials are mentioned by National Clinical Trial (NCT) number, and details can be obtained online at http://clinicaltrials.gov/