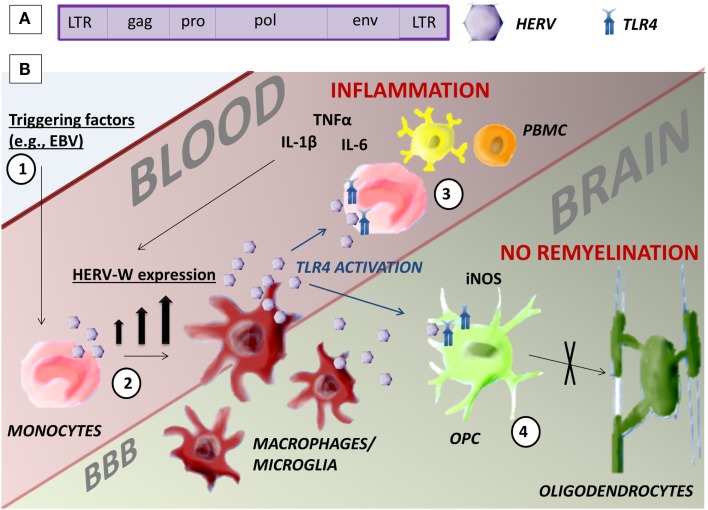
Figure 1.
Human endogenous retrovirus. (A) HERV gene structure. (B) Possible mechanism of action of HERV-W/MSRV in monocytes that could be pathogenic in MS. (1) Environmental triggering factors, such as EBV infection, induce the expression of HERV-W in monocytes. (2) The differentiation of monocytes in macrophages and microglia increases the presence of HERV-W. (3) HERV-W activates TLR4-induced inflammation in the blood and further increases HERV-W expression. (4) TLR4 inhibits the maturation of OPC in oligodendrocytes in the brain with consequent lack of remyelination.