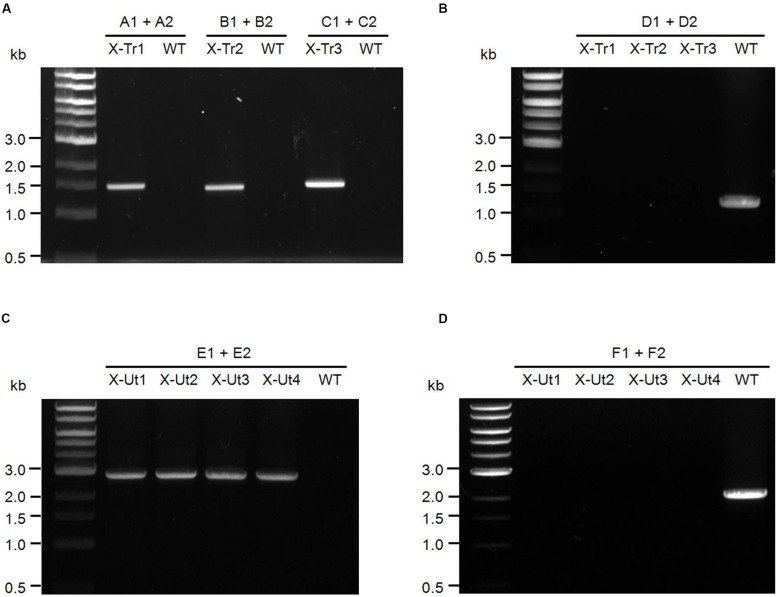
FIGURE 3.
Test of insertion of heterologous genes and chromosomal segregation for Synechocystis strains. (A) Primers upstream and downstream of the xylose transporter genes xylE (A1–A2), galP (B1–B2), and glf (C1–C2) were used to confirm the presence of the inserts in the respective transformants (Figure 2A) and also in the WT strain as the negative control. In the presence of the templates, primers A1–A2, B1–B2, and C1–C2 produced fragments of ∼1.48, ∼1.40, and ∼1.42 kb, respectively. (B) Primers upstream and downstream of intact neutral site 1 (D1–D2) were used to examine the chromosomal segregation for respective transformants (Figure 2A) along with the WT strain as a positive control. In the absence of uninterrupted neutral site 1, primers D1–D2 failed to produce PCR products in the transformants, whereas the WT strain yielded a ∼1.20-kb product. (C) Primers upstream and downstream of the xylose catabolic genes xylAB (E1–E2) were used to examine the insert in respective transformants (Figure 2B) and also in the WT strain as the negative control. In the presence of the template, primers E1–E2 produced a product of ∼2.85 kb. (D) Primers upstream and downstream of intact neutral site 2 (F1–F2) were used to check the chromosomal segregation for respective transformants (Figure 2B) along with the WT strain as the positive control. In the absence of uninterrupted neutral site 2, primers F1–F2 failed to produce PCR products in the transformants, whereas the WT strain yielded a ∼1.93-kb product.