Figure 2. Polypeptides with many putative effector modules and representative complexes.
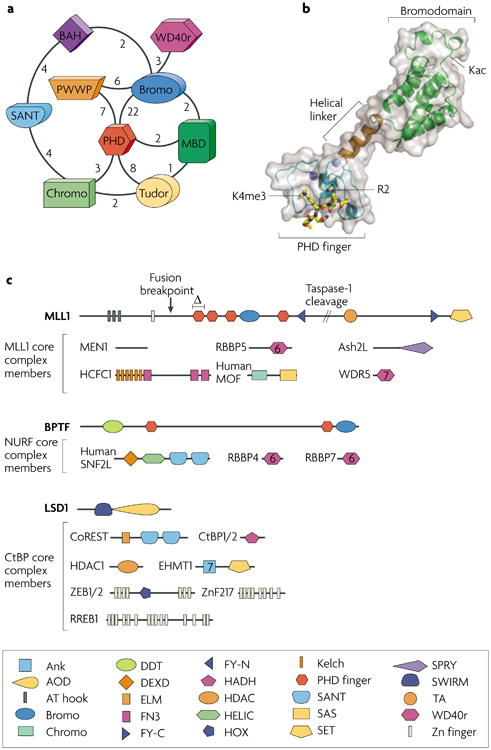
a | The coexistence of possible effector module domains within single polypeptides is depicted schematically, with the number of instances of linkage for any two domains within the human proteome listed near the line connecting them. The SMART database was used as the source of these linkages, and redundant entries were removed. b | A structurally characterized example of two linked effector domains is provided by the structure of a BPTF module that comprises a PHD finger, a helical linker and a bromodomain, with a trimethylated Lys4 of histone H3 (H3K4me3) peptide bound to the PHD finger85. The acetyl-Lys (Kac)-binding pocket on the bromodomain is shown, as well as residues R2 and K4me3 of the H3 peptide. c | Chromatin metabolism complexes, exemplified by the MLL1 (ref. 122), NURF103,123 and CtBP11 core complexes, have multiple putative effector domains. The predicted domain structure of subunits of the complex members are shown as a linear arrangement from N to C terminus. Chromatin-associated domains, most of which are modification sensitive, are coloured as in panel a, and are shown with additional predicted domains given in the key. The portion of the MLL1 protein that is cleaved by taspase-1 to yield two functional fragments (MLL1-N and MLL1-C) is shown. A frequent breakpoint at which fusion partners are appended and a domain deletion (Δ) that causes certain leukaemias are also depicted on the MLL1 domain structure. Ash2L, Set1–Ash2 histone methyltransferase complex subunit; BAH, bromo-adjacent homology domain; BPTF, bromodomain PHD finger transcription factor; Bromo, bromodomain; Chromo, chromodomain; CoREST, corepressor to the RE1 silencing transcription factor; CtBP, C-terminal binding protein; EHMT1, euchromatic histone-Lys N-methyltransferase-1; HCFC1, host cell factor C1; HDAC1, histone deacetylase-1; LSD1, Lys-specific demethylase-1; MBD, methyl-CpG binding domain; MEN1, multiple endocrine neoplasia-1; MLL1, mixed lineage leukaemia; MOF, males absent on first histone acetyltransferase; NURF, nucleosome remodelling factor; PHD, plant homeodomain; PWWP, PWWP motif protein of the Royal superfamily; RBBP, retinoblastoma binding protein; RREB1, Ras responsive element binding protein-1; SNF2L, sucrose non-fermenting-2-like ATPase; WD40r, WD40 repeat; WDR5, WD repeat domain-5; ZEB1/2, zinc finger E-box binding homeobox-1/2; ZnF217, zinc finger protein-217.
