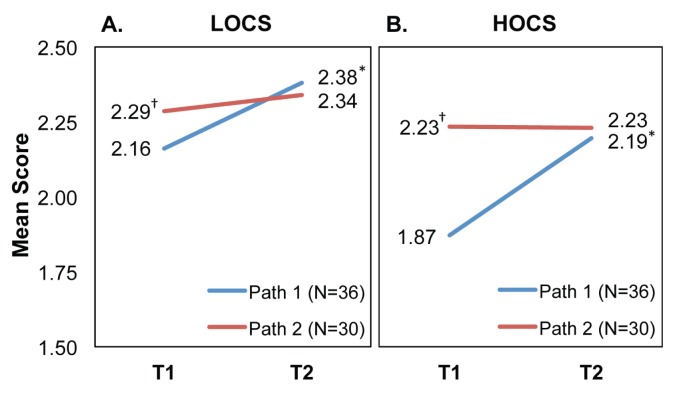
FIGURE 2.
Direct evidence of learning from a rubric-guided evaluation of embedded student assignments in Path 1 (CURE) and Path 2 (ARE). Rubrics were developed using a 3-point performance scale (1 = needs work, 2 = satisfactory, 3 = excellent) and employed to assess student oral presentation slides for Path 1 and Path 2 from the first term (T1) and second term (T2) of the curriculum (for rubrics, see Appendix 9). Rubric items were categorized as (A) LOCS or (B) HOCS (4, 19). For Path 1, there were 14 LOCS rubric items at T1 and another 14 items at T2. For Path 2 T1 and T2, there were 8 and 10 LOCS rubric items, respectively. With respect to HOCS rubric items, for Path 1 there were 15 and 17 at T1 and T2, respectively. For Path 2, there were 14 HOCS rubric items at T1 and another 14 items at T2. Data points on graphs represent the mean score at each time point for each Path. At T1, the mean scores for Path 2 (red lines) were significantly higher († p < 0.05) than Path 1 (blue lines) for both LOCS (A) and HOCS (B). The mean scores for Path 1 (blue lines) at T2 were significantly higher (* p < 0.05) than the mean scores at T1 for both HOCS and LOCS items, while Path 2 students (red lines) did not demonstrate measureable gains between these two time points. LOCS = lower-order cognitive skills; HOCS = higher-order cognitive skills; CURE = course-based undergraduate research experience; ARE = apprentice-based research experience.