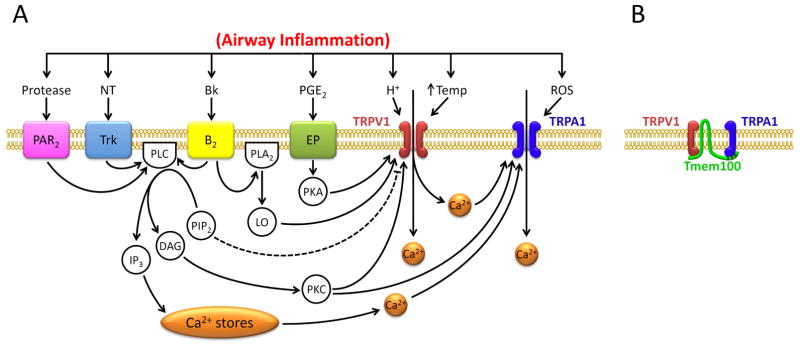
Figure 4.
Hypothesized mechanisms involved in the TRPA1-TRPV1 interaction in pulmonary sensory neurons. A: functional interaction between TRPA1 and TRPV1 during airway inflammation. Dashed line depicts an inhibitory pathway. Bk, bradykinin; B2, bradykinin B2 receptor; DAG, diacyglycerol; EP, prostanoid EP receptors; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; LO, lipoxygenase products; NT, neurotrophins; PAR2, protease-activated receptor-2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2 ; PLC, phospholipase C; PLA2, phospholipase A2; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Temp, temperature; Trk receptors, tryosine receptor kinase receptors A and B. B: potential physical interaction between TRPA1 and TRPV1 subunits in a heteromeric A1/V1 channel complex (Modified from reference 53). Tmem100, a two-transmembrane adaptor protein. See text for details.