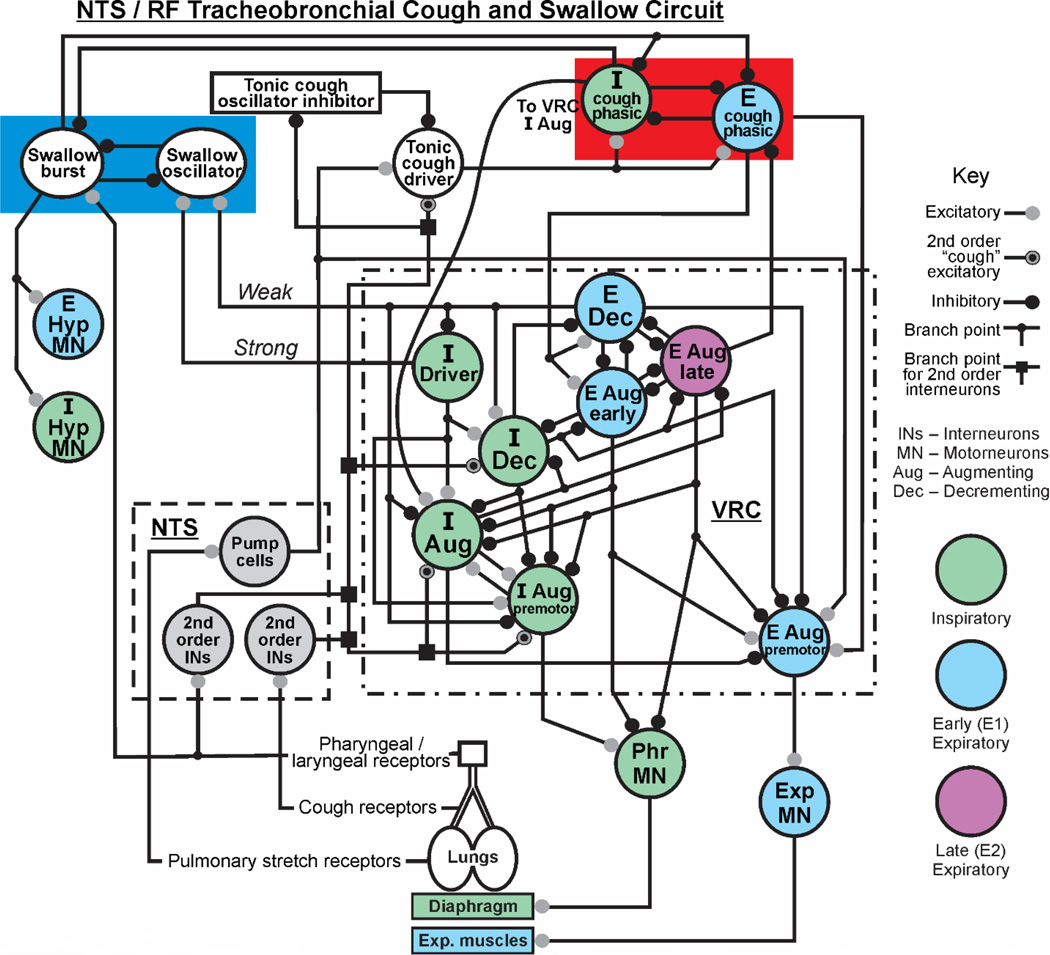
Figure 1. Proposed model of NTS/RF circuit for airway protection.
This circuit incorporates hypotheses on the coordination of cough and swallow, and preliminary results from recordings of NTS neurons. In the left section of the upper red box, a swallow oscillator circuit consisting of swallow burst and oscillator neurons is represented [1]. This circuit inhibits phasic cough inspiratory and expiratory neurons proposed to form a cough oscillatory network in the NTS/RF. The left side of the figure also shows excitatory drive to hypoglossal motoneuron pools from the swallow burst population. Preclinical experiments have identified NTS/RF neurons that are candidates for each population in the red box. The terms weak and strong represent synaptic excitation from the Exp Dec and I Driver populations, respectively, to the swallow oscillator population. These processes have been modeled [1]. Abbreviations: I-inspiratory, E-expiratory, Dec-decrementing, Aug-augmenting, VRC ventral respiratory column, Hyp-hypoglossal.