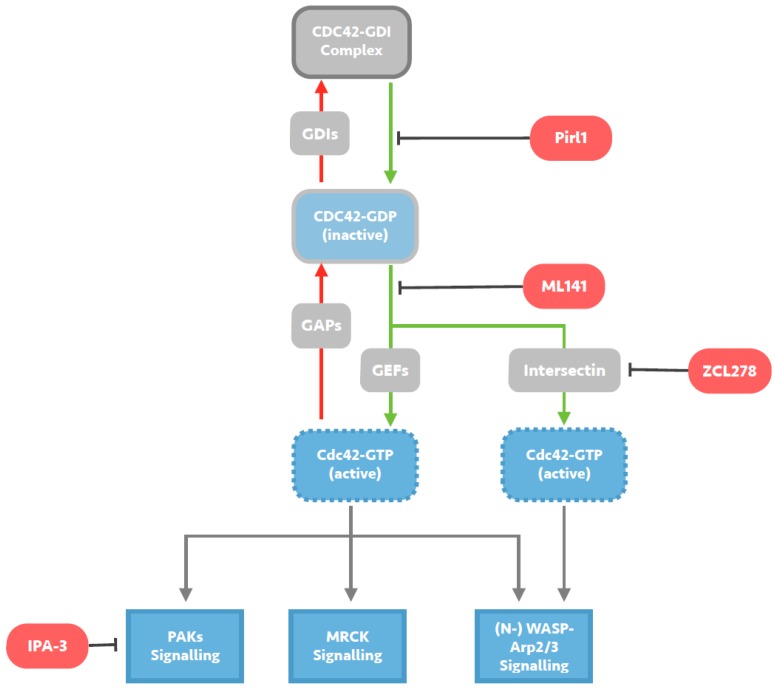
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of small molecule inhibition of Cdc42 signalling. Cdc42 activity is regulated by cycling from a GTP-bound active state to a GDP-bound inactive state. Guanine exchange factors (GEFs) such as Intersectin, promote the exchange of GDP for GTP and activate Cdc42, whilst GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) catalyse the intrinsic GTPase function and inactivate Cdc42. Guanine nucleotide-dissociation inhibitors (GDIs) sequester GDP-bound Cdc42, maintaining a pool of inactive Cdc42. Pirl1 is a small molecule inhibitor of actin assembly thought to act by inhibiting activation of Cdc42/GDI complexes, precluding guanine nucleotide exchange on Cdc42 and any subsequent interaction with downstream effectors. ML141 is a selective reversible non-competitive allosteric inhibitor of Cd42, preventing GTP binding to the active site of Cdc42 without targeting any Cdc42-regulating molecules. ZCL278 acts by selectively blocking interactions between Cdc42 and the Cdc42-specific GEF Intersectin, likely predominantly preventing (N-) WASP-Arp2/3 signalling. IPA-3 is a small molecule inhibitor of downstream Cdc42 signalling, selectively inhibiting group 1 PAKs by targeting the auto-regulatory mechanism present in this group.