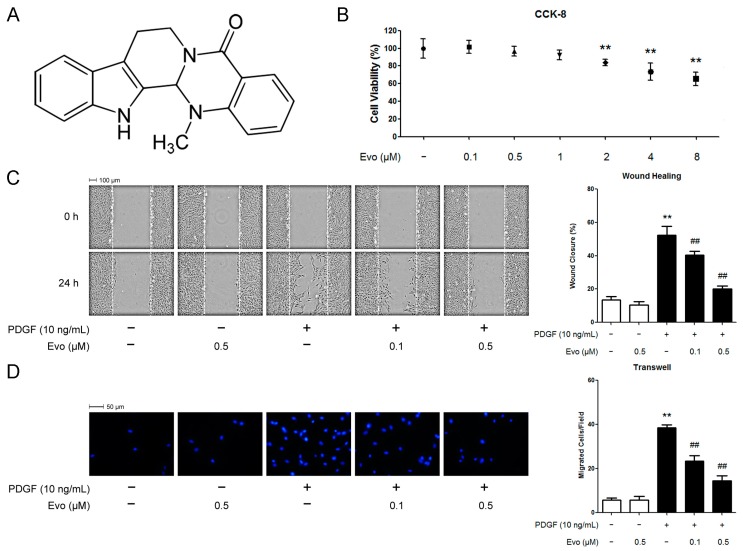
Figure 1.
Evodiamine cytotoxicity test and its effect on platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) -BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) migration. (A) Chemical structure of evodiamine; (B) Cytotoxicity test using evodiamine. VSMCs were cultured in medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, and treated with evodiamine at the indicated concentrations for 30 h. Cell viability was measured using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Results are expressed as cell viability relative to untreated controls; (C,D) Evodiamine inhibits PDGF-BB-induced VSMC migration; (C) Serum-starved cells were pretreated with evodiamine for 6 h before the stimulation of PDGF-BB for 24 h. Thereafter, cell migration was measured by using a wound healing assay; (D) Cells seeded into the inner chamber in serum-free medium were exposed to evodiamine with PDGF-BB for 6 h. Cell migration was thereafter measured by using a Boyden chamber assay. Blue color indicates cell nuclei stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Evo, evodiamine. Data are represented as mean values ± SD of three independently prepared samples each with five measurements. ** p < 0.01 compared with the control group; ## p < 0.01 compared with the PDGF-BB-stimulated group.