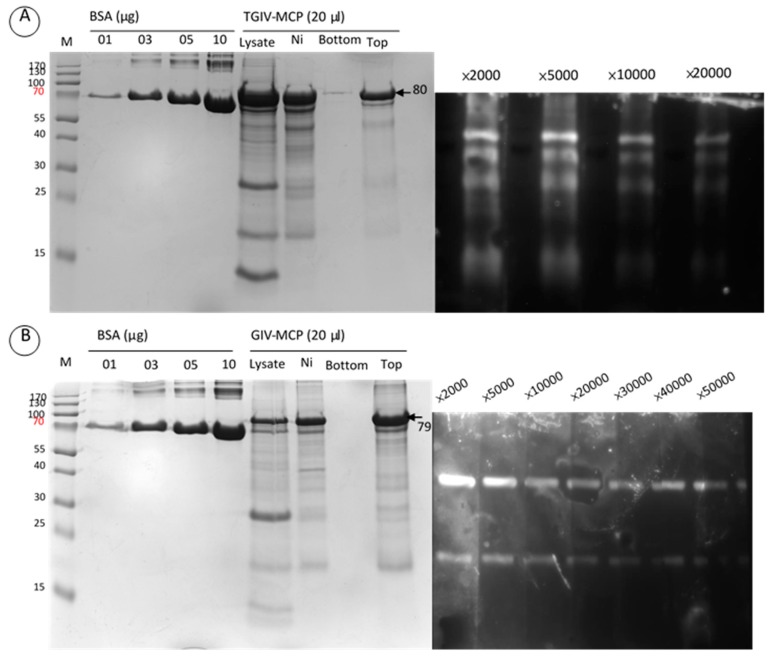
Figure 2.
Generation of anti-TGIV–MCP and anti-GIV–MCP polyclonal antibodies. The purification of recombinant MCP proteins and the specificity of the polyclonal antibodies are shown in the left and right panels, respectively. Left panels: Recombinant TGIV–MCP (A) and GIV–MCP (B) proteins were purified by Ni–NTA column (Ni), followed by centrifugation in centricon filter to displace imidazole in the lysis buffer. The purified recombinant proteins were used to immunize rabbit to generate polyclonal antibodies against TGIV–MCP and GIV–MCP, respectively. Top: the purified recombinant proteins; Bottom: the flow-through waste. Right panels: Western blotting was carried out to verify the specificity of the polyclonal antibodies generated from the recombinant proteins. Recombinant TGIV–MCP and GIV–MCP proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane, respectively. Western blotting was conducted with anti-TGIV-MCP (A) or anti-GIV–MCP (B) antisera. The TGIV–MCP antiserum was diluted in PBS at 2000, 5000, 10,000 and 20,000 folds, and the GIV–MCP antiserum was diluted in PBS at 2000, 5000, 10,000, 20,000, 30,000, 40,000 and 50,000 folds.