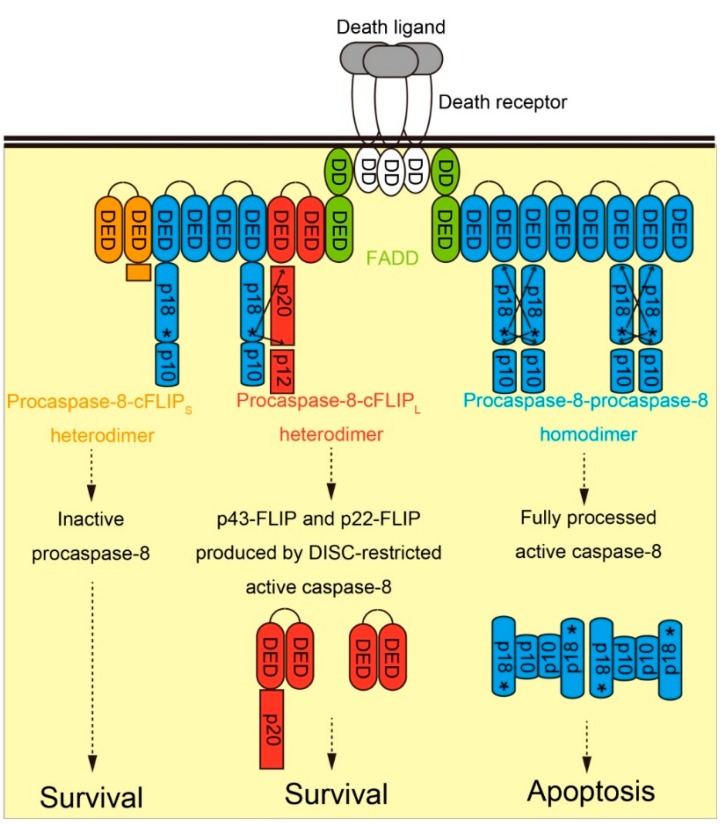
Figure 2.
Functional role of cFLIP during classical death receptor-mediated extrinsic apoptosis pathway. Upon stimulation by death ligand (gray), death receptor (white) forms trimer and activated. Adaptor protein FADD (green) then binds to activated death receptor via DD-DD interaction. Subsequently, DED-containing proteins including procaspase-8 (blue), cFLIPL (red), and cFLIPS (orange) are recruited to death receptor-bound FADD via DED-DED interaction, thereby forming DISC. Fully processed active caspase-8, generated by procaspase-8 homodimerization, activates effector caspases and induces apoptosis. Procaspase-8-cFLIPL heterodimerization results in the production of p43-FLIP and p22-FLIP but does not process procaspase-8, leading to cellular survival. In contrast, procaspase-8-cFLIPS heterodimerization inhibits the activation of procaspase-8 and prevents apoptosis.