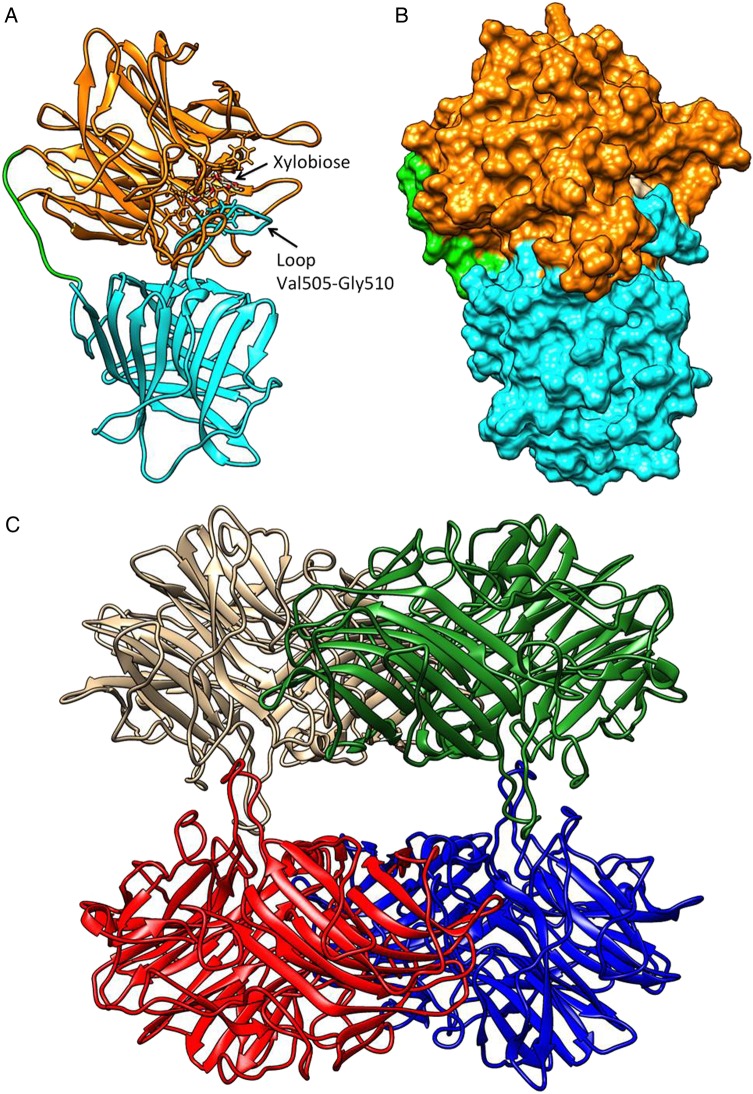
Fig. 4.
WXyn43 homology models for monomers of the two-domain enzyme (A and B), and the tetrameric form (C). In (A) the catalytic domain is shown in orange, the C-terminal domain in cyan and the inter-domains loop in green. A xylobiose is bound in the active site, and the loop putatively interacting with xylotriose is indicated. In (B), the active-site cavity is shown in surface representation using the same color scheme. In (C), the hybrid homology model of the homo-tetramer is shown: chain A in brown, chain B in blue, chain D in green and chain C in red. Interactions between chains A–D and B–C make compact dimers, while the interactions A–C and B–D stabilize the tetramer (see also Supplementary data, Table SV). Molecular graphics and analyses were performed with the UCSF Chimera v1.8.1 package (Pettersen et al. 2004).