Figure 1.
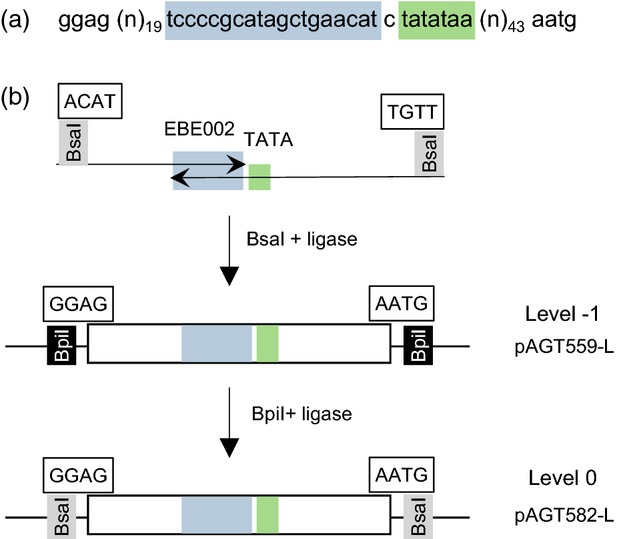
Design and cloning procedure of the synthetic transcription activator-like effector-activated promoters (STAPs).(a) general sequence of the STAPS. The constant designer transcription activator-like effector (dTALE)-binding site (EBE002) is highlighted in blue and the TATA box in green. The atg triplet at the end of the promoter corresponds to the translation start codon. The degenerate sequences upstream and downstream of the constant region are indicated by (n)19 and (n)43 respectively.(b) The STAPs cloning procedure. The library was synthesized using two degenerate oligonucleotides overlapping the constant region and cloned into a level –1 Golden Gate vector. Subsequent cloning into a level 0 vector allowed elimination of aberrant products (e.g. dimers) and false positives. The level 0 vectors can then be used for assembly into transcription units.
