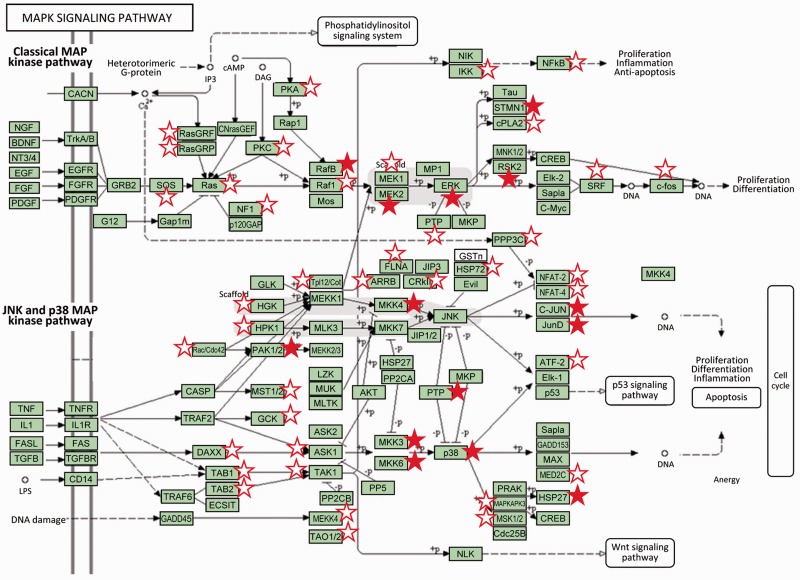
Figure 2.
Classical and JNK/p38 MAP kinase pathways (modified from KEGG pathways). Proteins for which one or more sites were detected phosphorylated in resting cells or cells after TCR activation are marked with a star. Filled stars indicate the observation of a significant phosphorylation change after lymphocyte activation (P adj value < 0.05, 0.65 < fold change > 1.5). MAP kinases play a major role in the processing of the signals originated by different external stimuli which ultimately trigger cell responses such as proliferation, cell division and differentiation and apoptosis (17, 18). Components of the MAP kinase pathway are central on the signal transmission pathways triggered by activation of the lymphocyte T receptor including p38, which is activated by ZAP-70, or the components of the classical Ras/Raf/MEK/Erk MAP kinase cascade which activation involves the proteins SOS and RasGRP (upper part of the graphic). Activation by SOS is directed by its translocation through the GRB2-LAT complexes, while RasGRP is phosphorylated by PKC which in turn is activated by the DAG second messenger liberated by the activity of PLC-γ (18).