Fig. 7.
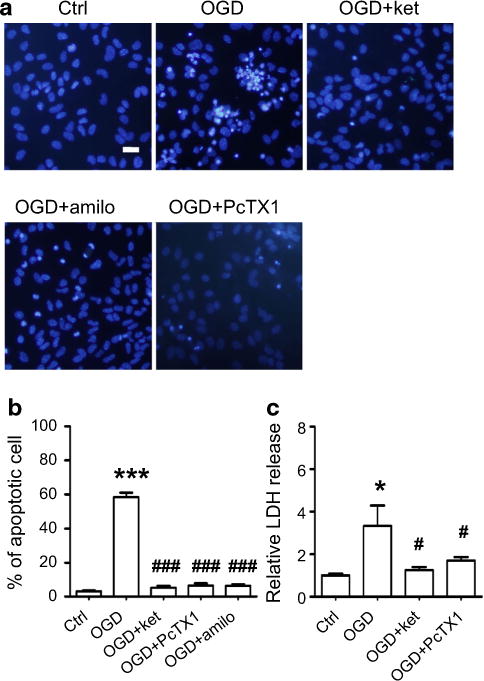
Inhibition of either NMDAR or ASIC1a protected neurons from OGD-evoked cell death. a Representative images of Hoechst-33342 stained neurons showing that OGD induced typical apoptotic cell death (upper middle panel). Cell death was largely prevented by inhibition of NMDARs with ketamine (upper right panel), or by inhibition of ASIC1a with amiloride (lower left panel) or PcTX1 (lower right panel). Scale bar is 20 μm. b Summarized data showing that OGD treatment of hippocampal neuronal cultures induced a large amount of apoptotic cell death (58.4 %; n = 4), which is much higher than that of control (3.1 %; n = 7; ***p < 0.005). However, when NMDARs were blocked with ketamine, this OGD-evoked cell death was reduced to 5.3 % (n = 4; ###p < 0.005). When ASIC1a was blocked with PcTX1 or amiloride, the cell death rate was reduced to 6.6 % (n = 4) and 6.5 % (n = 5), respectively. ASIC1a antagonists demonstrated very effective neuro-protective properties in the OGD treatment of hippocampal cultures (###p < 0.005). c LDH release is also measured in this set of experiments. Consistent with the data on apoptotic cell death, OGD induced high levels of LDH release (3.3-fold; n = 4) compared to control (*p < 0.05). As expected, NMDAR antagonists and ASIC1a antagonists suppressed LDH release in OGD-treated cultures to 1.3-fold (n = 4) and 1.7-fold (n = 6) that of control, respectively. #p < 0.05 compared with OGD treatment.
