Figure 3. Ethanol-induced redistribution of tight junction proteins in the distal colon is blocked by Gln supplementation.
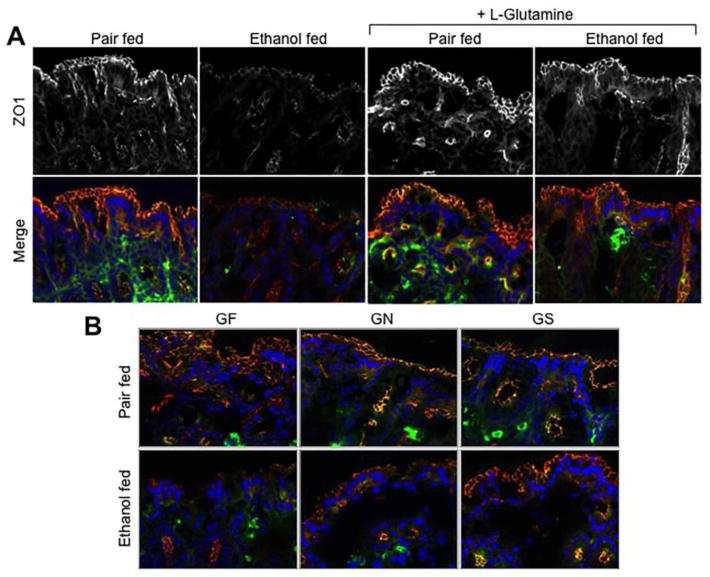
A: Adult mice were fed Lieber-DeCarli liquid diet with (Ethanol fed) or without (Pair fed) ethanol and with or without Gln supplementation. Cryosections of distal colon were stained for occludin (green) and ZO1 (red; gray in the upper panels) by immunofluorescence method, and the nucleus stained with Hoechst dye (blue). B: Mice were fed a Gln-free amino acid diet with (Ethanol fed) or without (Pair fed) ethanol (1–6% over 4 weeks) and without (GF) or with 8.4 g/L (GN) or 16.8 g/L (GS) Gln supplementation. Cryosections of distal colon were stained for occludin (green) and ZO1 (red) by immunofluorescence method, and the nucleus stained with Hoechst dye (blue).
