Figure 8. Gln supplementation ameliorates chronic ethanol-induced liver injury.
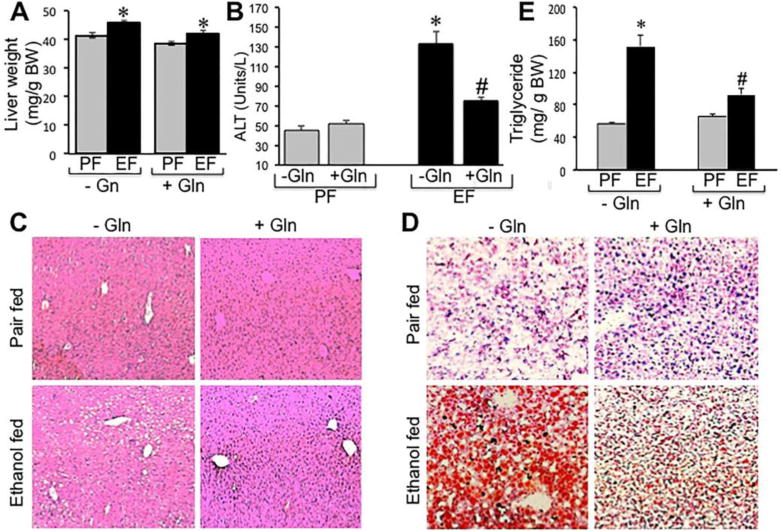
Adult mice were fed Lieber-DeCarli liquid diet with (EF) or without (PF) ethanol and with or without Gln supplementation. Liver weights (A) were recorded, plasma ALT levels measured (B) and H & E stained paraffin sections of liver were imaged by light microscopy (C). Cryosections of liver were stained with Oil Red-O and imaged by light microscopy (D), and liver extracts were assayed for triglyceride content. Values are mean ± SE (n = 6). Asterisks indicate the values that are significantly (p<0.05) different from values for corresponding non-ethanol pair fed group, and the hash tags indicate the values that are significantly (p<0.05) different from corresponding values for “− Gln” group.
