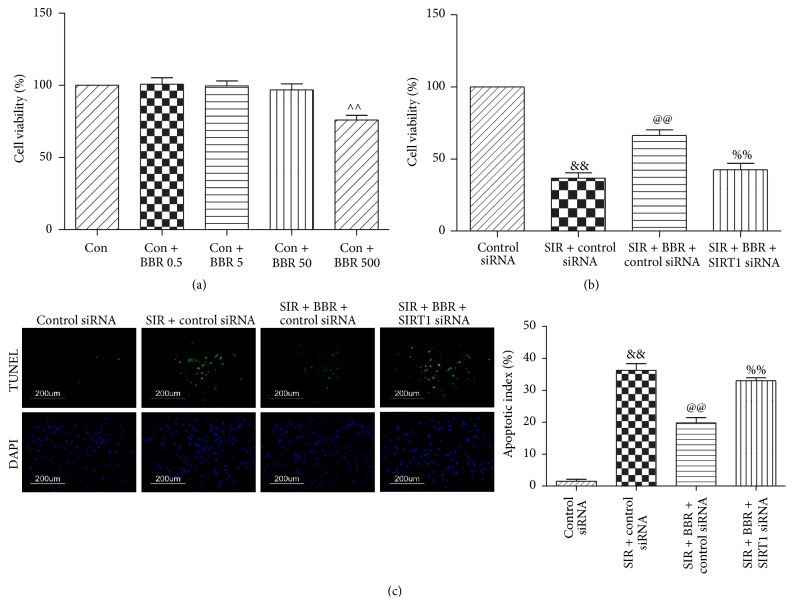
Figure 9.
Effects of BBR and SIRT1 siRNA on cell viability and the apoptotic index in SIR-injured cardiomyocyte. H9C2 cardiomyocytes were exposed to control siRNA or SIRT1 siRNA and then treated with BBR (50 μmol/L for 8 hr). Next, cells were subjected to simulated ischemia/reperfusion (SIR, 2 hr/4 hr) treatment. Then, cell viability and apoptotic index were measured. (a) Viability of cardiomyocytes was determined by MTT and was calculated by dividing the optical density of samples by the optical density of Sham control. (b) Viability of cardiomyocytes determined by MTT. (c) Left: representative photomicrographs of in situ detection of apoptotic cardiomyocytes by TUNEL staining. Green fluorescence shows TUNEL-positive nuclei; blue fluorescence shows nuclei of total cardiomyocytes, original magnification ×400. Right: percentage of TUNEL-positive nuclei. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, n = 8/group. ∧∧ P < 0.01 versus Con group, && P < 0.01 versus control siRNA group, @@ P < 0.01 versus SIR + control siRNA group, and %% P < 0.01 versus SIR + BBR + control siRNA group.