Figure 4. Lesion correlates of posterior aphasia syndromes.
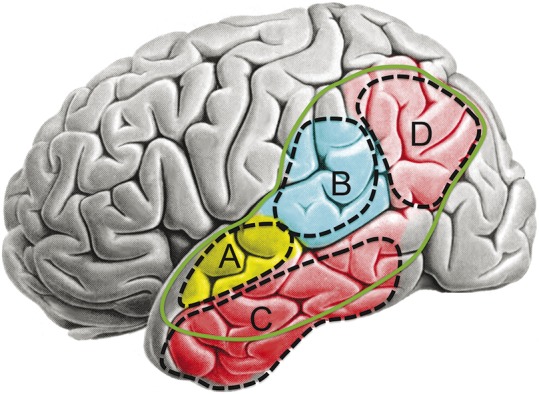
Bilateral damage restricted to region A produces pure word deafness. Strokes centered on region B produce conduction aphasia, and neurodegeneration in this region produces a similar syndrome called logopenic-variant primary progressive aphasia. Damage localized to the semantic system (regions C or D) produces transcortical sensory aphasia, and neurodegeneration focused on region C produces a similar syndrome known as semantic-variant primary progressive aphasia. The solid green line indicates the territory in which larger lesions produce Wernicke aphasia, a syndrome that combines damage to region B with partial damage to the surrounding semantic system. Background brain image reproduced with permission from Springer.
