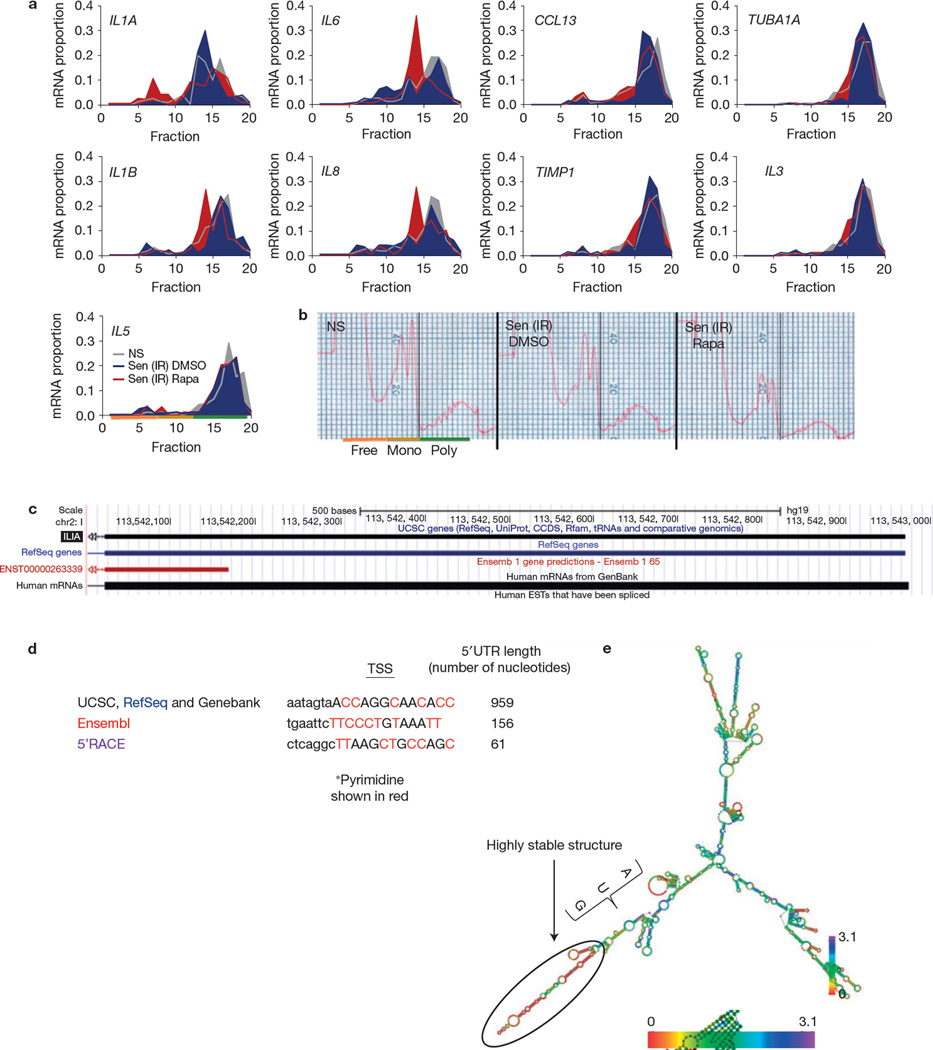
Figure 5.
Rapamycin inhibits IL1A translation. (a) Senescent (ionizing radiation; Sen (IR)) HCA2 cells were treated for 7 days with rapamycin (Rapa) or DMSO followed by 1 day in serum-free media, after which cells were collected and mRNA was collected for polysome profiling as described in the Methods. qPCR was performed on each fraction for IL1A, IL6, CCL13, TUBA1A, IL1B, IL8, TIMP1, IL3 and IL5 mRNA (one representative experiment is shown). Fractions 1–7: free RNA; 8–12: 40–60S; 13–20: polysome. (b) Polysome profiles used to determine the translated fractions; representative polysome traces are shown. NS, non-senescent. (c) Using the UCSC genome browser sequence, analysis of the IL1A gene was performed to determine potential start sites of transcription. (d) Potential transcription start sites (TSSs) and their 5’UTRs are shown from various sources, including the determination based on 5’RACE (see c). Transcription start site sequences start at the capital letter and pyrimidines are shown in red. (e) IL1A mRNA minimum free energy structure was determined using the default parameter obtained from the University of Vienna RNAfold web service (http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/RNAfold.cgi). Scale represents the organizational entropy. The presence of a highly stable structure upstream of the start codon is detected. 5’RACE was performed once. For a and b, shown is one representative of two independent experiments, each with triplicate cell culture samples. For raw data, see Supplementary Table 4.