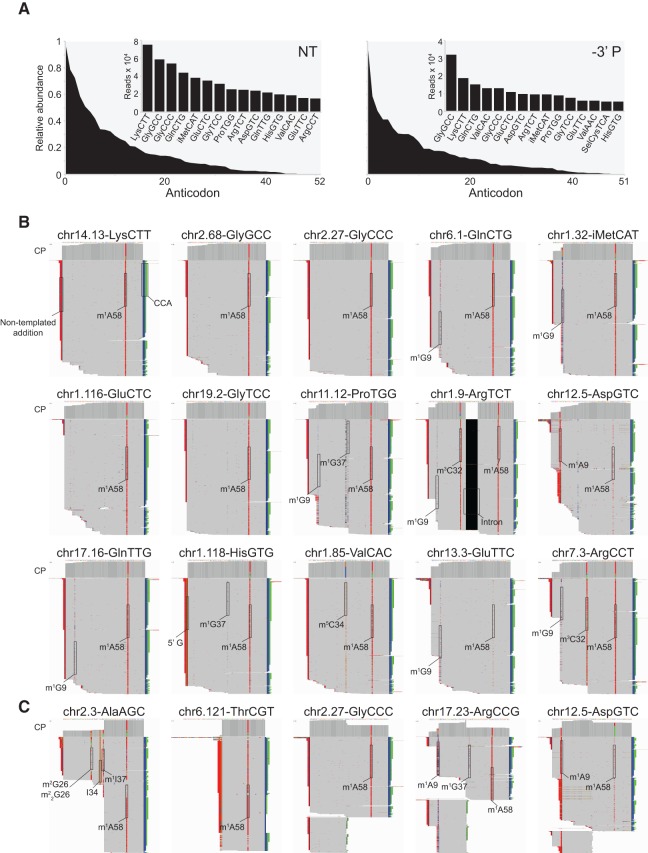
FIGURE 7.
TGIRT-seq identifies full-length mature tRNAs and tRNA fragments in human plasma. (A) Relative abundance of tRNAs identified in RNA-seq data sets constructed with TeI4c RT for total plasma RNA prepared by the Direct-zol method without (NT; combined DS1–3) or with treatment to remove 3′ phosphates (–3′ P; combined DS4–6). The plots show tRNAs with 10 or more mapped reads grouped by anticodon and rank-ordered by read count. The 15 most abundant tRNAs based on anticodon are shown in the bar graph insets. (B) IGV screen shots showing coverage plots (CP; above) and alignments (below) of reads for abundant full-length mature tRNAs identified in the NT data sets. The tRNAs were ordered by abundance as in the left panel of A. For cases in which multiple loci encode tRNAs with the same sequence, tRNA reads were distributed equally among different tRNA loci for the IGV alignments. (C) IGV screen shots showing coverage plots and alignments of reads for representative 3′-tRNA halves in the NT data sets (AlaAGC and ThrCGT) and 5′-tRNA halves in the –3′ P data sets (GlyCCC, ArgCCG, and AspGTC). The arrow at the top indicates the boundaries and 5′–3′ orientation of the mature tRNA on the chromosomal DNA sequence. In order to fit the entire alignment in one panel, genes with >1000 mapped reads were down-sampled to 1000 reads in IGV. Reads were sorted by start site on the chromosome. Nucleotides matching the genome sequence are shown in gray, and mismatches are shown as different colors (A, green; C, blue; G, brown; and T, red). Mismatches at the 5′ end of the reads are likely due to nontemplated nucleotide addition by the TGIRT enzyme to the 3′ end of the cDNAs. Mismatches due to misincorporation at known sites of post-transcriptional modifications are highlighted with the name of the modification. Modifications: I, inosine; m1A, 1-methyladenosine; m3C, 3-methylcytidine; m5C, 5-methylcytidine; m1G, 1-methylguanosine; m2G, N2-methylguanosine; m22G, N2,N2-dimethylguanosine.