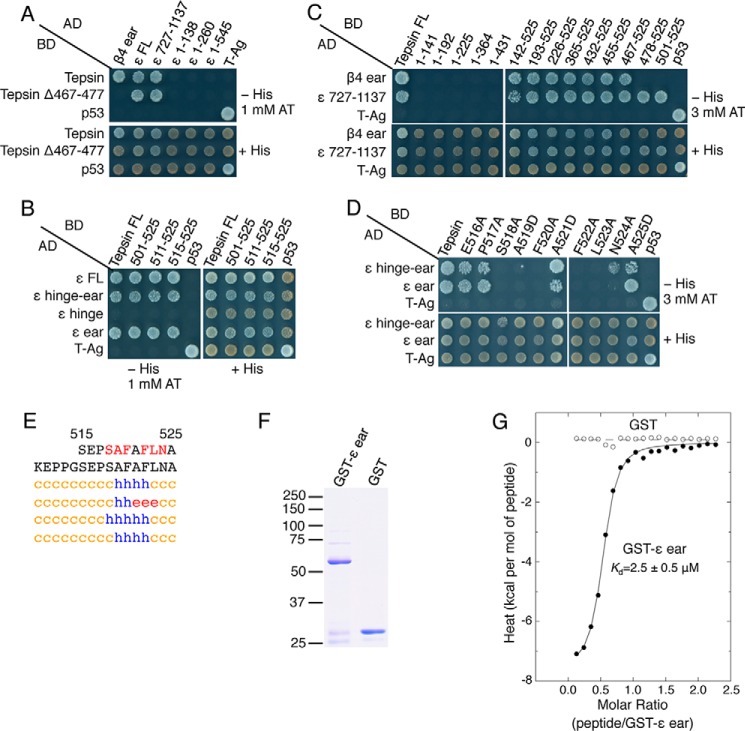
FIGURE 6.
Identification of a second tepsin motif that mediates interactions with the AP-4 ϵ-ear domain. A–C, Y2H analysis of the interaction of full-length and N- and C-terminally truncated forms of AP-4 ϵ with full-length tepsin and a series of N- and C-terminally truncated forms of tepsin (schemes shown in Fig. 2, A and C). D, Y2H analysis of the interaction of ϵ-hinge-ear and ϵ-ear constructs with tepsin mutants having single amino acid substitutions in the segment spanning amino acids 516 to 525. E, secondary structure prediction of the tepsin C-terminal region including segment 515–525 by the methods described in the legend to Fig. 1B. F, SDS/PAGE analysis and Coomassie Blue staining of GST-ϵ ear and GST proteins used in ITC assays. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated at left. The GST-ϵ ear migrates with an apparent molecular mass of 60 kDa. G, ITC analysis of the interaction of ϵ-ear-binding peptide SEPSAFAFLNA with GST-ϵ ear. The binding isotherm depicts the normalized integrated heat change (kcal/mol of injected peptide) as a function of the molar ratio of peptide to GST-ϵ ear. Data were fit to a one-site binding model. The indicated Kd value for the tepsin peptide-GST-ϵ ear interaction represents the mean ± S.D. of three determinations performed with different preparations of recombinant protein.