FIGURE 3.
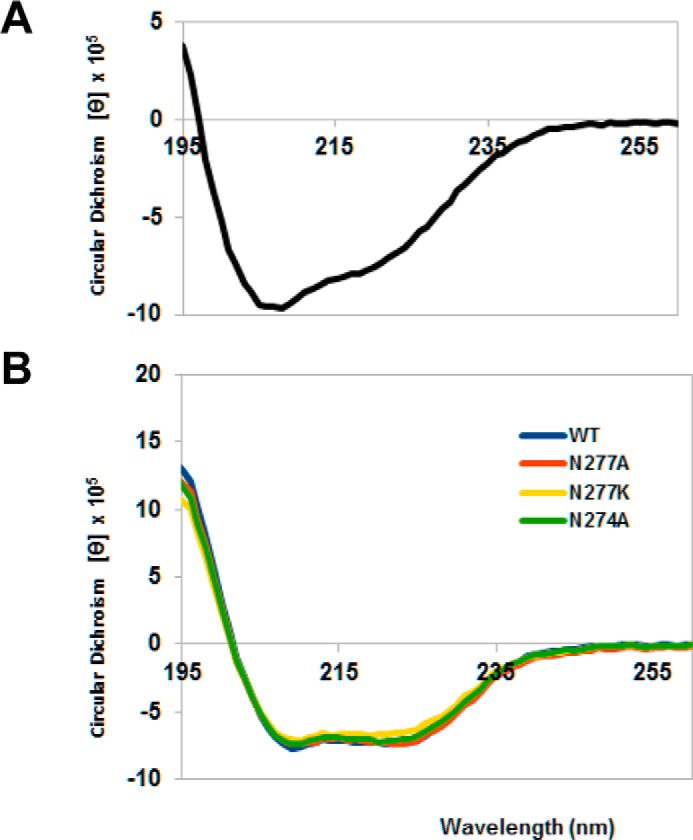
Circular dichroism spectra of the central domain of colicin D and LepB (wild-type and mutant proteins). Far ultraviolet spectra were measured in 20 mm phosphate buffer, pH 7.5, using a Chirascan Spectrometer (Applied Photophysics Ltd., Leatherhead, UK) and recorded at 20 °C from 260 to 195 nm in a 1.0-mm optical path length quartz cell. Spectra were an average of three scans and were corrected for the buffer baseline. Concentrations of each proteins were determined using molar extinction coefficients at 280 nm (49,515 cm−1 m−1 and 20,970 cm−1 m−1 for LepB proteins and the central domain of colicin D, respectively), and the circular dichroism spectra obtained in millidegrees were converted to mean residue molar ellipticity ([θ], MRV are deg cm2 dmol−1). A, the spectrum of colicin D central domain showed characteristic double minima at 208 and 222 nm, indicating the presence of α-helices. B, the spectra of mutated LepB, measured in the presence of 0.25% reduced (non-UV absorbing) Triton X-100, were found to be comparable in pattern and intensity to wild-type (WT) LepB, indicating that the point mutations did not alter the secondary structure of the proteins.
