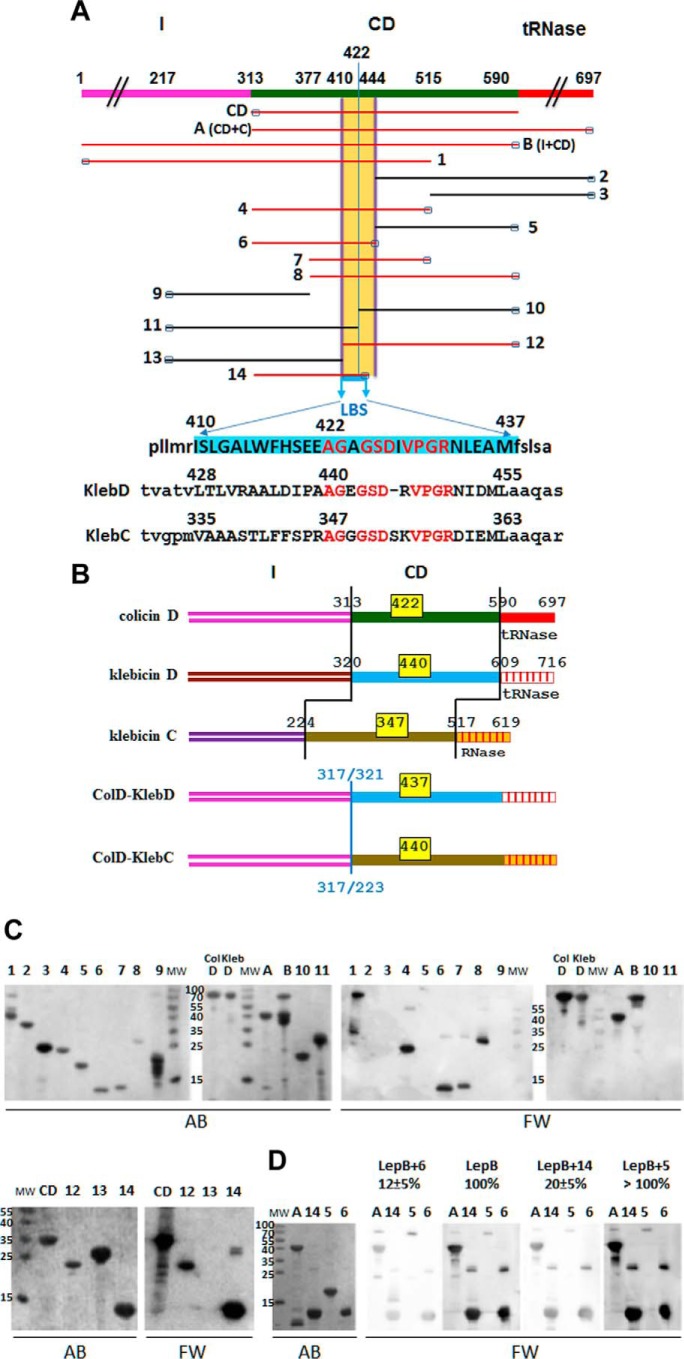
FIGURE 4.
Physical maps of truncated/deleted derivatives of colicins D and hybrid colicin/klebicin derivatives. In vitro interaction of the LepB signal peptidase with truncated colicins D or partially deleted central-domain derivatives. A, the domain structure of wild-type (FS) colicin D (formed by the import domain (I), CD, the toxic tRNase domain) is shown in different colors. Regions present in the 17 colicin D derivatives (CD, A (CD+C), B (I+CD), and those numbered 1–14) are indicated. Amino acid positions at the start and stop of the truncated proteins are indicated on the map of colicin D. The small black rectangles at the N or C terminus indicate the location of the His6 tag in each colicin derivative used for protein purification. The location of the LBS is delineated, and the 28-amino acid-long sequence is highlighted in blue. Colicin D constructs carrying the LBS sequence are shown in red. The equivalent putative LBS sequences in tRNase klebicin D (KlebD) and RNase klebicin C (KlebC) are shown. Identical residues in the three LBS sequences are written in red letters. B, color-coded domain structures of wild-type colicin D, klebicins D and C, and the two hybrid colicin/klebicins constructed in this work are shown. In hybrid colicin/klebicin molecules, the intact N-terminal import domain of colicin D is followed by the central and catalytic domains of klebicin D (starting at positions 321) or those of klebicin C (starting at positions 225). The positions of residues delimiting each domain in wild-type molecules or the position of in-frame fusion points in the hybrids are given. The location of the LBS consensus motif, with the positions of the first amino acid, is given for each wild-type or hybrid colicin molecules (yellow boxes). C, polypeptides of full-size colicin D (ColD), colicin D derivatives, or klebicin D (KlebD) were separated on a 15% SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and detected by Amido Black staining (AB). Those interacting with purified wild-type LepB were detected with anti-LepB antiserum (Far Western blotting (FW)). Molecular masses (MW) of reference proteins are given in kDa. The numbering of derivatives is the same as in A. D, analysis of the LepB binding to the central domain of colicin D in the presence of competing colicin D derivatives including the LBS (constructs A, 6, and 14) or not (construct 5). Proteins were separated on a 15% SDS-PAGE and treated as above except that LepB was preincubated with the competing colicin derivatives for 30 min before incubation with the membrane. The effect of the preincubation on the efficiency of LepB interaction as measured with anti-LepB antiserum was quantified and expressed as a percentage of the value measured with wild-type LepB without preincubation with any colicin derivative (100%).