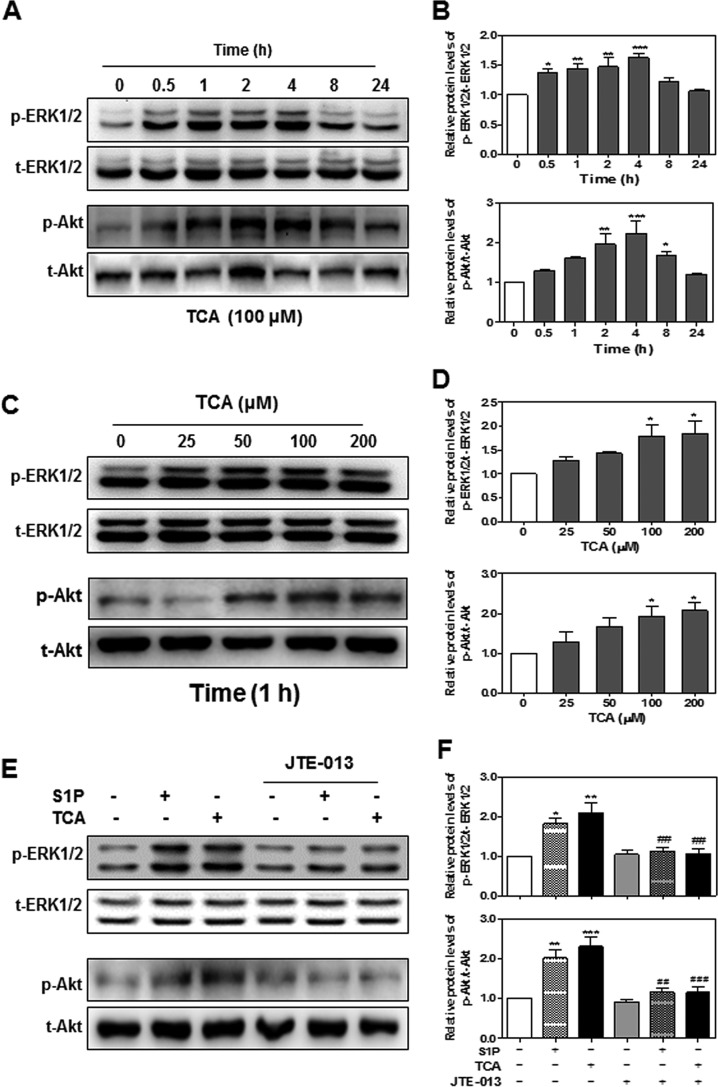
FIGURE 12.
The effect of TCA on ERK and Akt activation in HuCCT1 cells. A and B, time course of TCA-induced ERK and Akt activation. HuCCT1 cells were cultured in serum-free medium overnight and then treated with TCA (100 μm) for different treatment periods (0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, or 24 h). C and D, TCA-induced dose-dependent activation of ERK and Akt. HuCCT1 cells were cultured in serum-free medium overnight and then treated with different concentrations of TCA (0, 25, 50, or 100 μm) for 1 h. E and F, the effect of JTE-013 on TCA-/S1P-induced ERK and Akt activation. HuCCT1 cells were cultured in serum-free medium overnight and pre-treated with JTE-013 (10 μm) for 1 h and then treated with S1P (100 nm) or TCA (100 μm) for 1 h. At the end of each treatment, cells were harvested and total protein was isolated. The protein levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK), total ERK1/2 (t-ERK), phosphorylated Akt1/2/3 (p-Akt), and total Akt1/2/3 (t-Akt) were detected by Western blot analysis. A, C, and E, representative images of the immunoblots for p-ERK, t-ERK, p-Akt, and t-Akt are shown. B, D, and F, relative levels of p-ERK/t-ERK and p-Akt/t-Akt. Values represent the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. Statistical significance relative to the vehicle control: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; relative to S1P or TCA treatment groups: ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001.