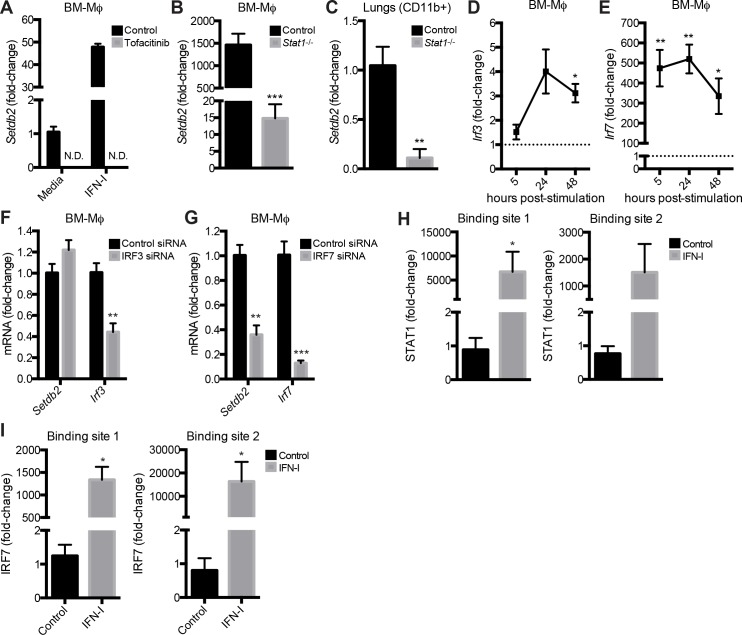
Fig 2. Setdb2 expression by Mϕ is dependent on JAK-STAT pathway and IRF7.
(A-C) RT-PCR of Setdb2 in BM-Mϕ (A, B) and CD11b+ cells (C) from IAV-infected lungs. (A) Untreated and IFN-I-stimulated BM-Mϕ were treated with a vehicle control or the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib at the time of stimulation. (B) Control and Stat1 -/- BM-Mϕ were stimulated with media or IFN-I for 5 hours. (A, B) Data are mean ± SEM relative to unstimulated cells; n = 3 independent experiments. (C) CD11b+ cells were isolated from the lungs of control and Stat1 -/- mice inoculated with IAV (1 x 104 PFU). Data are mean ± SEM relative to control cells on day 4 post-infection; n = 8–12 mice. (D, E) RT-PCR of Irf3 (D) and Irf7 (E) in control BM-Mϕ stimulated with IFN-I for the indicated time course. Data are mean ± SEM relative to unstimulated cells; n = 2–3 independent experiments (F, G) RT-PCR of Setdb2 and Irf3/Irf7 in BM-Mϕ treated with control, IRF3, or IRF7 siRNA and stimulated with IFN-I for 24 hours. Data are mean ± SEM relative to cells treated with control siRNA; n = 3 independent experiments. (H, I) ChIP analysis of STAT1 (H) and IRF7 (I) binding in the Setdb2 promoter in control and IFN-I-stimulated BM- Mϕ after 24 hours. Data are mean ± SEM relative to IgG control; n = 2–3 independent experiments. N.D.; not detected. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.