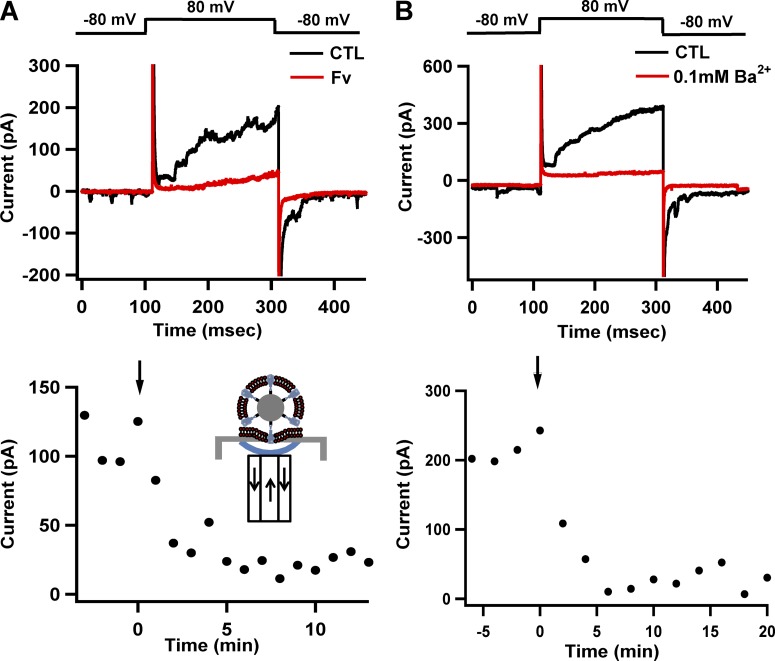
Figure 6.
Electric recordings of tetrameric Kv channels in bSUMs. (A) Specific inhibition of the channel activity by Fv. After the formation of the gigaohm seal, test pulses from a holding potential of −80 to 80 mV for 200 ms were delivered once every minute. The gigaohm seal was formed in the cell-attached mode. As a result of membrane disruption on the outside (see B and Fig. 1 E), recordings were made in the inside-out mode (black trace in the top panel). When 100 µg/ml Fv was perfused into the extracellular side of the channels for 2 min while the membrane was held at 0 mV (inset diagram to the bottom), the channel activity was almost completely blocked (red trace). The bottom panel displays the time-dependent inhibition of KvAP activity via Fv. The black arrow points to the time of Fv application. The arrows in the cartoon of the bottom show the solution flow (arrows) to and from the bottom droplet (blue line) right under the hole of the planar electrode in the perfusion system. The results represent typical experiments from many of our routine tests to confirm the identity of the recorded channels. (B) Breakdown of the bSUMs on the outer side (above the planar electrode) after the formation of the gigaohm seal avoids the space-clamp problem. After the recorded currents became stable (black trace in the top panel) for at least 10 min, 0.10 mM Ba2+ was perfused into the top partition, and the currents were recorded 2 min later. The top panel shows two traces before and after Ba2+ addition (black and red traces, respectively). The bottom panel displays the time-dependent inhibition of KvAP activities by Ba2+. The black arrow indicates the time when Ba2+ was applied. These results are typical of four experiments. For these experiments, the solution in the top partition (the intravesicular side of the bSUMs and the intracellular side of the channels) contained 80 mM NaCl, 200 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 2 mM CaCl2, and 10 mM HEPES/KOH, pH 7.4; the bottom partition (the extravesicular side of the bSUMs and the extracellular side of the channels) had 10 mM NaCl, 200 mM KCl, 60 mM KF, 20 mM EGTA, and 10 mM HEPES/KOH, pH 7.4.