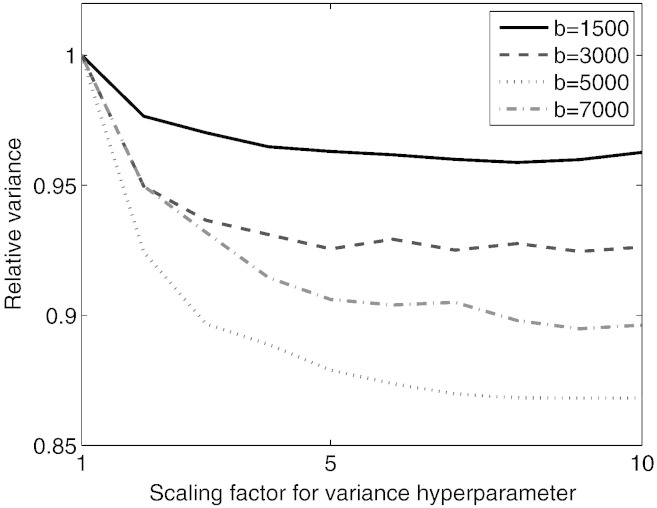
Fig. 3.
Plot showing how the error variance (as assessed by sum-of-squared differenced of paired images with opposing PE directions) relative to that of no Q-space smoothing depends on the level of Q-space smoothing. The Q-space smoothing is achieved by multiplying the GP-error-variance by a factor greater than 1, and is shown for the range 1 to 10. It can be seen that it has a relatively minor effect on “normal” b-values of 1500, but that it has a substantial effect on data acquired with higher b-values (5000 and 7000). The plot indicates that by choosing a value of 10 close to optimal results are obtained for all b-values. Data set was used for this figure.