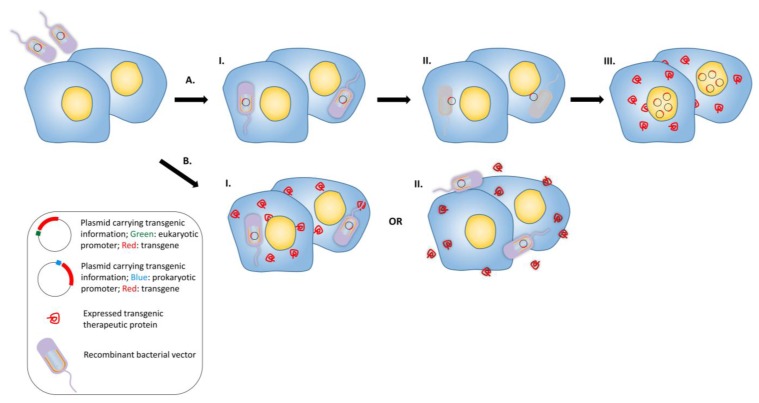
Figure 3.
Bactofection into tumors. (A) Bacteria are used as a vector to deliver the genetic information into the eukaryotic cell. Bacterial vectors that possess plasmid (each bacterial vector can carry multiple copies of transgenic plasmid) carrying a transgene are administered into the target tissue, I.: The vectors penetrate into the cells. II: Vectors undergo lysis and the plasmids are released into the cytoplasm, III: The released plasmids enter the nuclei and the therapeutic transgene is expressed by eukaryotic transcription and translation mechanisms; (B) Alternative gene therapy: recombinant bacterial vectors express the recombinant therapeutic protein in situ intracellularly or in the intercellular space. Recombinant bacterial vector that possess plasmid carrying the transgene are administered into the target tissue and either enter the cells or stay in the intercellular space; I: The transgene is expressed and secreted after entering the cell, or; II: Bacteria do not enter the eukaryotic cell, but express the therapeutic transgene in the intercellular space.