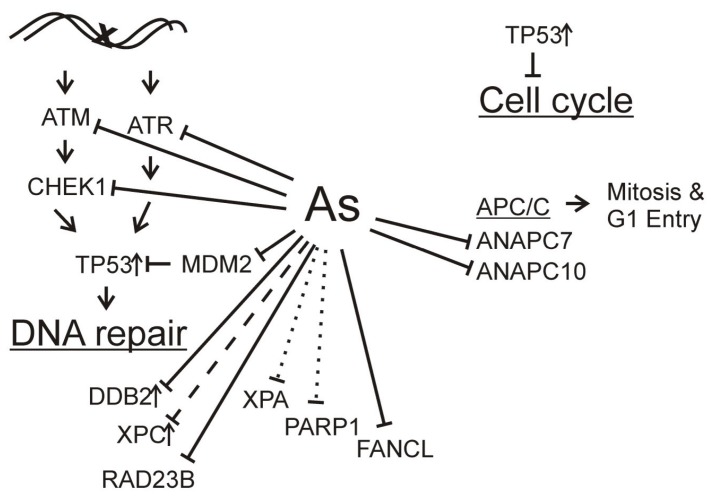
Figure 1.
Arsenic inhibition of DNA damage response. DNA damage normally leads to activation of signaling kinases converging through TP53 stimulating DNA repair gene expression and inhibition of cell cycle. Arsenite inhibits transcription (solid lines) of signaling kinase genes (ATM, ATR, CHEK1), MDM2, and downstream DNA repair genes DDB2 and RAD23B. Expression of XPC also is inhibited by arsenite (dashed line), as is function of XPA and PARP1 by displacing zinc from the zinc fingers in these proteins (dotted lines). These effects likely contribute to decreased nucleotide excision repair. FANCL transcription inhibition may lead to decreased interstrand crosslink repair. Arsenite also inhibits transcription of ANAPC7 and ANAPC10, components of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) consistent with arsenite disruption of mitotic progression.