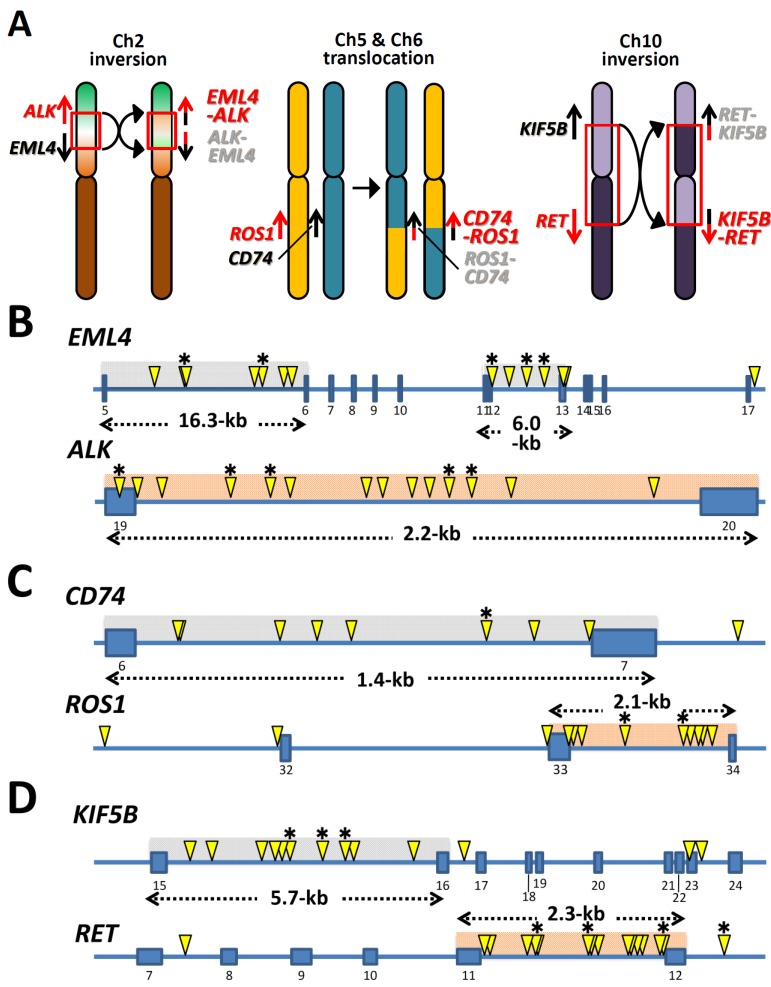
Figure 2.
Cluster of breakpoints in oncogenes and partner genes. (A) Chromosome inversion and translocation producing oncogene fusions. (B–D) Distribution of breakpoints in ALK and its major partner gene EML4 (B), ROS1 and its major partner gene CD74 (C), and RET and its major partner gene KIF5B (D). Yellow arrowheads indicate the locations of breakpoints for fusions in 41 Japanese LADC cases. All these cases were identified in a Japanese LADC cohort of 608 cases [8]. Breakpoints for chromosome rearrangements were identified by next-generation sequencing and/or genomic PCR analyses of tumor DNAs as previously described [9]. Breakpoint cluster regions are gray-hatched for partner genes and orange-hatched for oncogenes. Breakpoints in tumors of smokers are marked by asterisks.