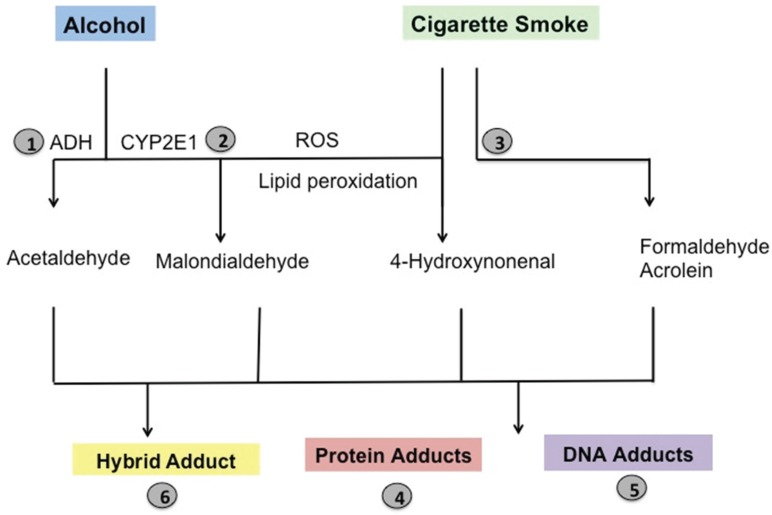
Figure 1.
Generation of lung aldehydes and adduct formation. Alcohol is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) to acetaldehyde (AA). But during chronic alcohol consumption, CYP2E1 is induced leading to generation of ROS like superoxide, hydrogen radical and hydrogen peroxide. This promotes lipid peroxidation and generation of malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE). Cigarette smoke itself contains high concentration of AA, acrolein and formaldehyde. In addition to this, smoking cigarettes also induces local inflammation in lung causing more generation of ROS. This further promotes lipid peroxidation generating more MDA and 4-HNE. Acetaldehyde and MDA could form hybrid adduct through Schiff base reaction when 2 mole of MDA react with 1 mole of AA to form a stable hybrid adduct [74,75,76,77].