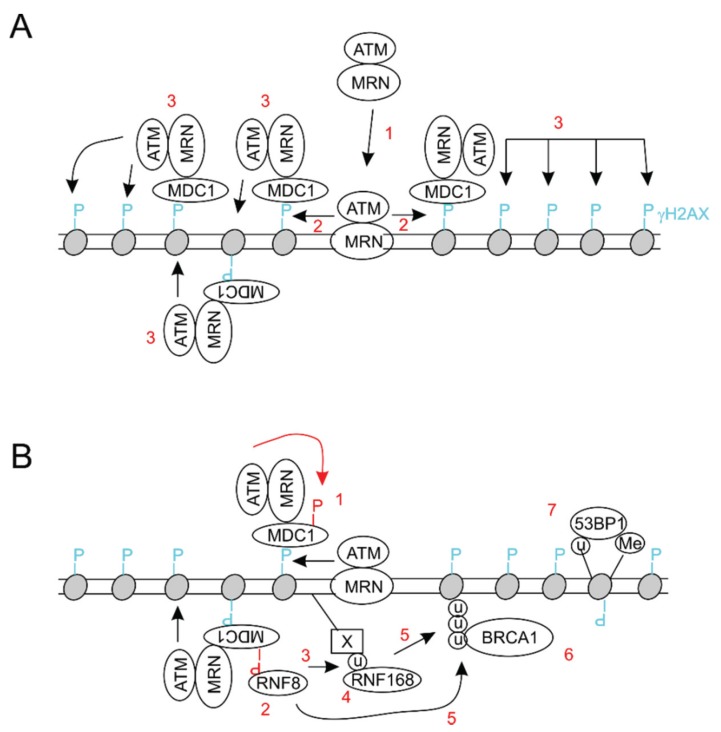
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the assembly of the double-stranded DNA break (DSB) repair complex. (A) The MRN complex recruits ATM to DSB (1), allowing ATM to phosphorylate S139 of H2AX (γH2AX) (2); and (3): MDC1 is subsequently recruited and the CK2-phosphorylated SDT motifs at the N-terminus of MDC1 interact with the MRN-ATM complex, resulting in the spread of the γH2AX domain. (B) The association of the MRN-ATM complex with MDC1 leads to ATM-mediated phosphorylation of MDC1 (1), RNF8 recruitment (2), RNF8-derived ubiquitination of unknown substrate (X) (3), and the binding of RNF168 (4); and (5): RNF8 and RNF168 coordinately ubiquitinate histone H2A/H2AX, paving the way for BRCA1 recruitment (6). The ubiquitination of H2A K15 together with H4 K20 methylation contribute to 53BP1 recruitment.