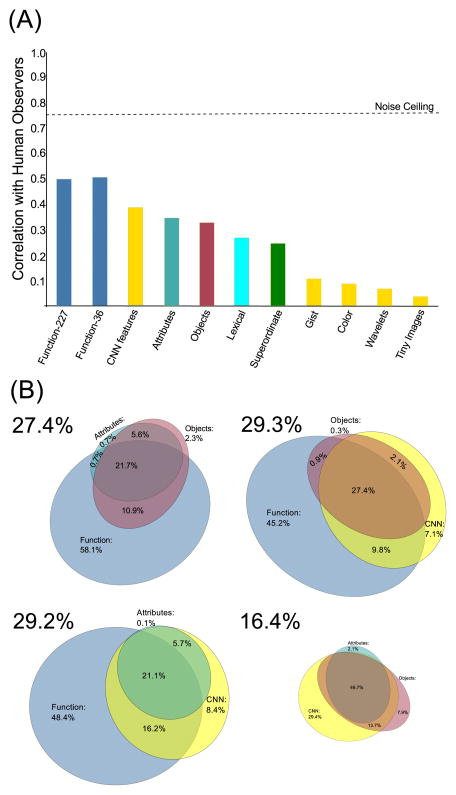
Figure 4.
(A) Correlation of all models with human scene categorization pattern. Function-based models (dark blue, left) showed the highest resemblance to human behavior, achieving 2/3 of the maximum explainable similarity (black dotted line). Of the models based on visual features (yellow), only the model using the top-level features of the convolutional neural network (CNN) showed substantial resemblance to human data. The object-based model, the attribute-based model, the lexical model and the superordinate-level model all showed moderate correlations. (B) Euler diagrams showing the distribution of explained variance for sets of the four top-performing models. The function-based model (comprehensive) accounted for between 83.3% and 91.4% of total explained variance of joint models, and between 45.2% and 58.1% of this variance was not shared with alternative models. Size of Euler diagrams is approximately proportional to the total variance explained.