Figure 1.
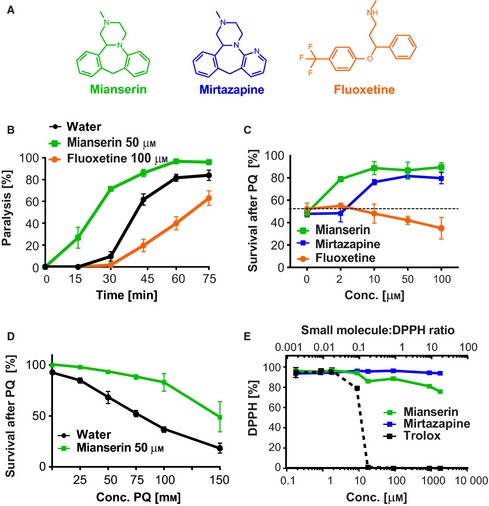
The atypical antidepressant Mianserin increases synaptic transmission and resistance to oxidative stress. (A) Structures of the atypical antidepressants Mianserin and Mirtazapine and the typical antidepressant Fluoxetine. (B) Mianserin increases and Fluoxetine decreases synaptic transmission as measured by aldicarb‐induced paralysis. Wild‐type L4‐stage animals were pretreated with 50 μm Mianserin or 100 μm Fluoxetine for 2 h, followed by 4 mm of the acetylcholine esterase inhibitor aldicarb. Aldicarb‐induced paralysis, a measure of synaptic transmission, was determined every 15 min and plotted in [%] (y‐axis) as a function of time in minutes [min] (x‐axis). (C) Antidepressant treatment affects the survival of Caenorhabditis elegans under conditions of oxidative stress. Wild‐type day 1 adults were treated with increasing concentrations of the indicated antidepressants, followed by 100 mm of the ROS generator paraquat on day 5. Survival of animals was determined 24 h later and plotted in [%] (y‐axis) as a function of antidepressant concentration [μm] (x‐axis). Dotted line shows the survival of untreated animals. (D) Mianserin treatment protects C. elegans from a range of paraquat concentrations. Wild‐type day 1 adults were treated with water or 50 μm Mianserin, followed by increasing concentrations of paraquat on day 5. Survival of animals was determined 24 h later and plotted in [%] (y‐axis) as a function of paraquat concentration [mm] ((x‐axis). (E) Antidepressants have no significant free radical‐scavenging activity. Increasing concentrations of either the indicated antidepressants or the ROS scavenger Trolox were incubated with 90 μm of the free radical DPPH. Reduction of DPPH [%] was monitored by measuring absorption at 520 nm (y‐axis) and plotted as the ratio of small molecule to DPPH (upper x‐axis) or the concentration of small molecule in μm (lower x‐axis). All error bars show SEM. for multiple, independent experiments. For additional data, see Fig. S1 (Supporting information). For detailed statistics, see Tables S1–S3 (Supporting information).
