Figure 1.
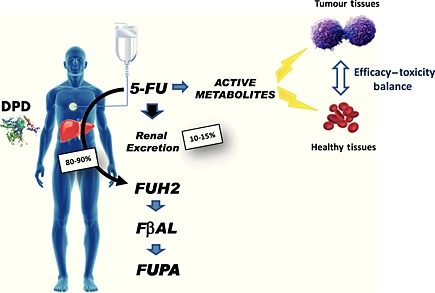
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) rapidly catabolizes more than 80% of the administered dose of 5‐FU to inactive metabolites. The remaining 5‐FU is distributed throughout the body and converted into nucleosides or deoxunucleosides then nucleotides or deoxynucleotides, including FdUMP, FdUTP and FUTP which display cytotoxic properties against TS, DNA and RNA respectively. DPD deficiency will increase the conversion of 5‐FU into active metabolites, thus triggering exposure of both healthy and tumor tissues
