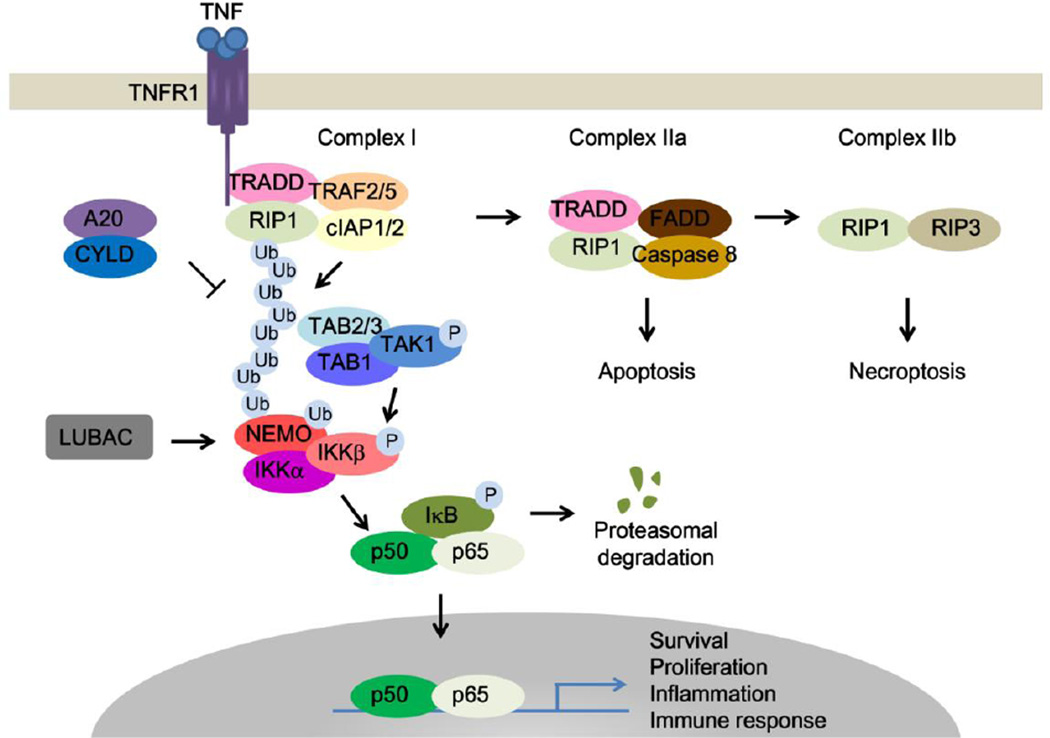
Figure 1. Activation of TNF signaling.
TNFα binding to TNFR1 causes Complex I formation by recruitment of TRADD, RIP1, TRAF2/5, cIAP1/2, and LUBAC. cIAP1/2 promotes K63-linked polyubiquitination of RIP1, whereas A20 and CYLD deubiquitinates RIP1. In the Complex I, K63-linked polyubiquitination of RIP1 mediates TAK1-TAB1-TAB2/3 complex recruitment. TAK1 is responsible for the phosphorylation and activation of IKK complex, resulting in IκBα degradation and NF-κB-mediated gene transcription. Inactivation of cIAP1 or deubiquitination of RIP1 by CYLD facilitates Complex I transition to Complex II. Complex IIa consists of TRADD, RIP1, FADD and caspase-8, which induces apoptosis. Inhibition of caspase-8 or FADD causes the formation of Complex IIb, ultimately leading to necroptosis.